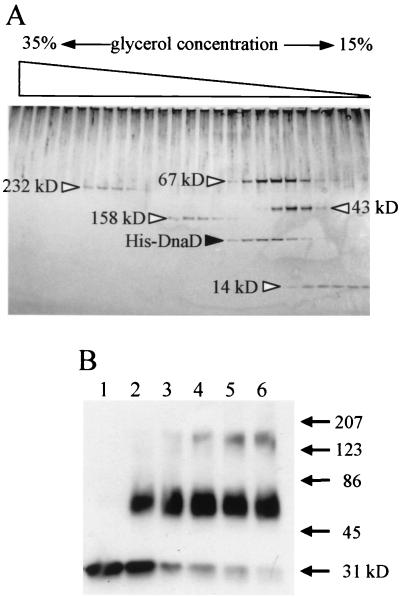
FIG. 1.
Analysis of DnaD-DnaD interaction in vitro by glycerol density-gradient centrifugation (A) and cross-linking (B). (A) The purified His-tagged DnaD protein (1.8 μg) was loaded with molecular mass (MM) markers on a glycerol density gradient (15 to 35%; 2.4 ml) containing buffer A (25 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 1 mM EDTA, 0.01% Nonidet P-40, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM dithiothreitol) with a cushion of 50% glycerol (0.1 ml) at the bottom of the gradient. The proteins were separated by centrifugation for 12 h at 160,000 × g using a TLS55 rotor and Optima TL Ultracentrifuge (Beckman). After centrifugation, the density gradient was fractionated into 24 samples (100 μl in each). Proteins in the fractions were detected by silver staining after separation on a sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gradient gel (10 to 20%) by electrophoresis. MM markers shown by open triangles are follows: catalase (232 kDa), aldolase (158 kDa), bovine serum albumin (67 kDa), ovalbumin (43 kDa), and RNase A (14 kDa). (B) His-DnaD (1 μl; 220 ng/μl) was added into 50 μl of buffer A containing 0.01% glutaraldehyde to start cross-linking. After incubation at room temperature for 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 min (lanes 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6, respectively), each reaction mixture was mixed with 50 μl of 2× sample loading buffer and heated at 95°C for 5 min. Samples were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and visualized by immunoblotting using a rabbit anti-DnaD antiserum. Lane 1, without glutaraldehyde. MM markers are shown with arrows.