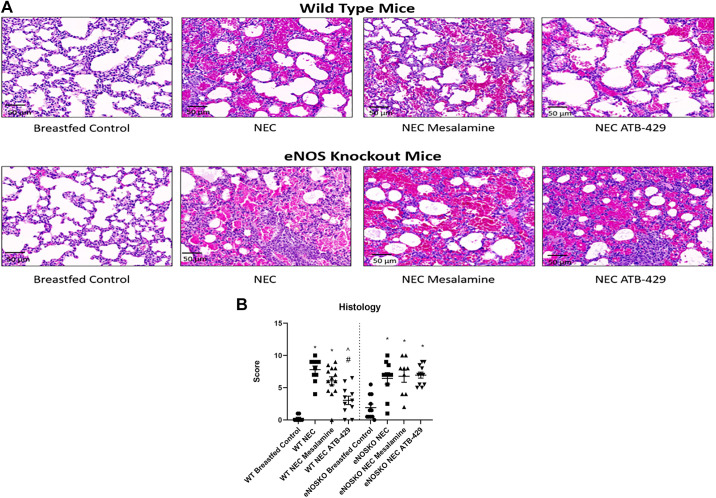
Figure 4.
ATB-429 reduces histologic lung injury in experimental NEC. At the conclusion of the experiment the right lower lobe of the lung was explanted, sectioned, and stained. Histologic injury was blindly scored using a modified injury scale from the American Thoracic Society as described in methods. A: representative photomicrographs of both WT and eNOSKO mice lung histology. Breastfed controls have thin healthy alveolar septa. NEC pups have severe injury with thickening of alveolar septa, neutrophil infiltrate, hemorrhage, and proteinaceous debris. Magnification ×20. B: experimental NEC caused a significant increase in lung injury in both WT and eNOSKO mice. ATB-429 attenuated the degree of pulmonary injury in WT mice, but not in eNOSKO mice. Statistical analysis was performed using Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn’s multiple-comparisons test. *P < 0.05 vs. Breastfed Control, #P < 0.05 vs. NEC, ^P < 0.05 vs. NEC Mesalamine. eNOSKO, endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice; NEC, necrotizing enterocolitis; WT, wild type.