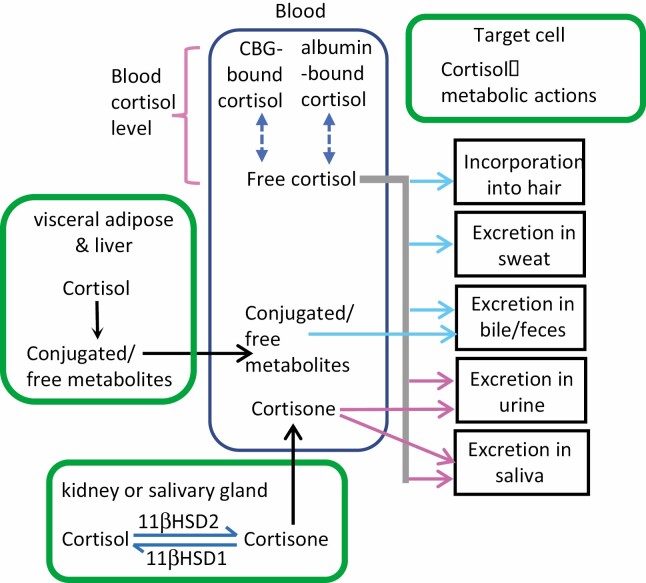
Figure 4.
The fates of blood cortisol after secretion by the adrenal glands. Nearly all cortisol circulates in blood bound to a chaperone protein, either corticosteroid binding globulin (CBG) or albumin. The remaining unbound (free) fraction is biologically active and diffuses into target tissues, where it (1) exerts metabolic effects, (2) is metabolized (eg, renal inactivation into cortisone by 11βHSD2 or additional hepatic conversions), (3) is incorporated into growing hair, or (4) is excreted in sweat, urine, or feces. The pink arrows denote tissues in which free cortisol and/or its metabolites can be measured using commercially available assays; the blue arrows indicate research assays. Free cortisol in blood can be measured commercially or calculated using serum cortisol, albumin, and CBG values.