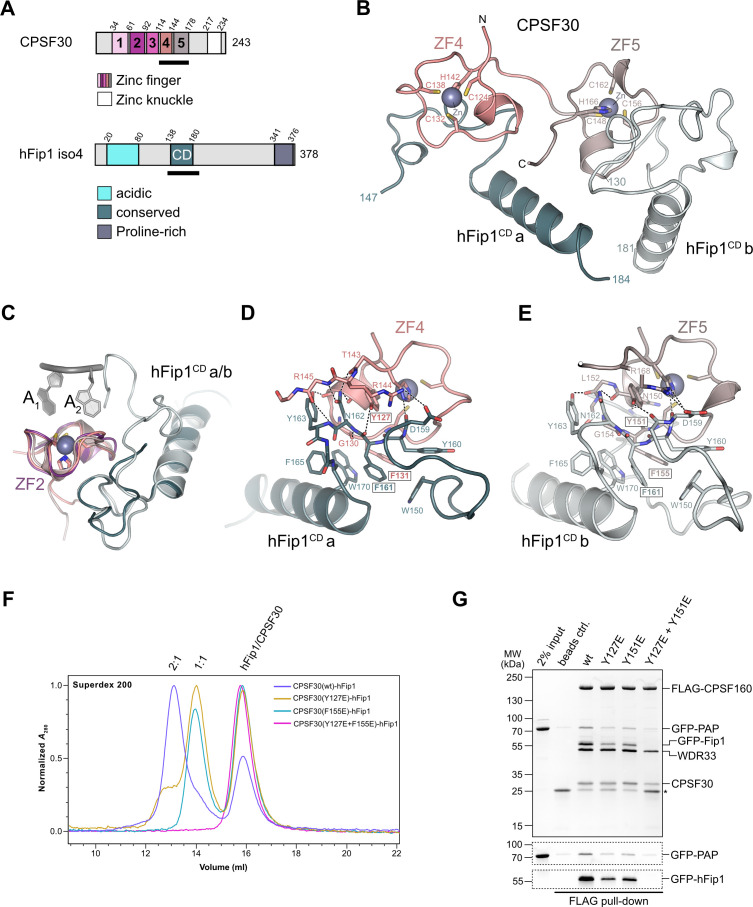
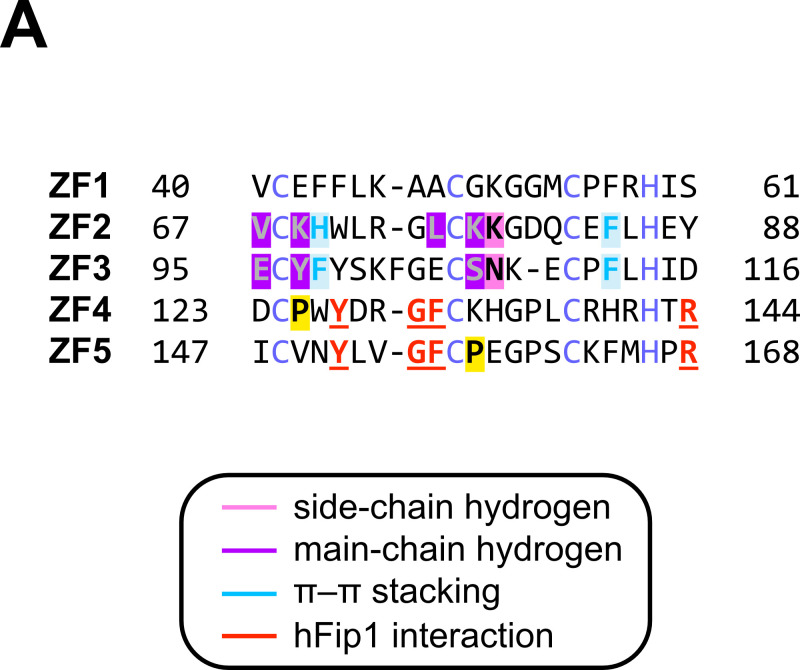
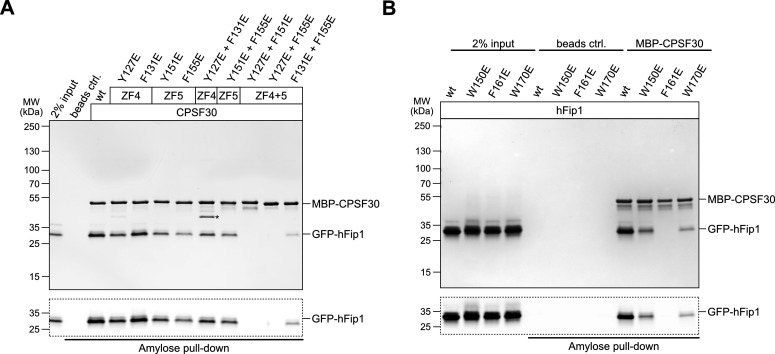
Figure 1. hFip1 interacts with CPSF30 with 2:1 stoichiometry.
(A) Schematic representation of the domain architecture of CPSF30 and hFip1. CPSF30 consists of five zinc finger (ZF) domains and a zinc knuckle domain. hFip1 isoform 4 comprises acidic, conserved, and proline-rich regions but lacks the RE/D region interacting with CF Im, as well as the R-rich region, which has been shown to bind U-rich RNA in hFip1 isoform 1 (Kaufmann et al., 2004). (B) Cartoon representation of the crystal structure of CPSF30ZF4–ZF5 in complex with two hFip1 fragments comprising the conserved domain (CD). (C) Superposition of CPSF30 ZF2 domain in complex with PAS RNA onto ZF4 and ZF5. (D) Detailed interaction interface of hFip1CD with CPSF30 ZF4. (E) Detailed interaction interface of hFip1CD with CPSF30 ZF5. (F) Size-exclusion chromatography coupled to multiangle static light scattering (SEC-MALS) chromatogram of MBP-CPSF30ZF4–ZF5 selective hFip1-binding mutants for stoichiometry analysis with GFP-hFip1. (G) In vitro pull-down analysis of FLAG-epitope-tagged mPSF comprising wild-type CPSF30 and its selective hFip1-binding mutants with GFP-PAP. Asterisk indicates anti-FLAG M2 antibody light chain. GFP-hFip1 and GFP-PAP are also visualized with in-gel GFP fluorescence (bottom).