FIGURE 2.
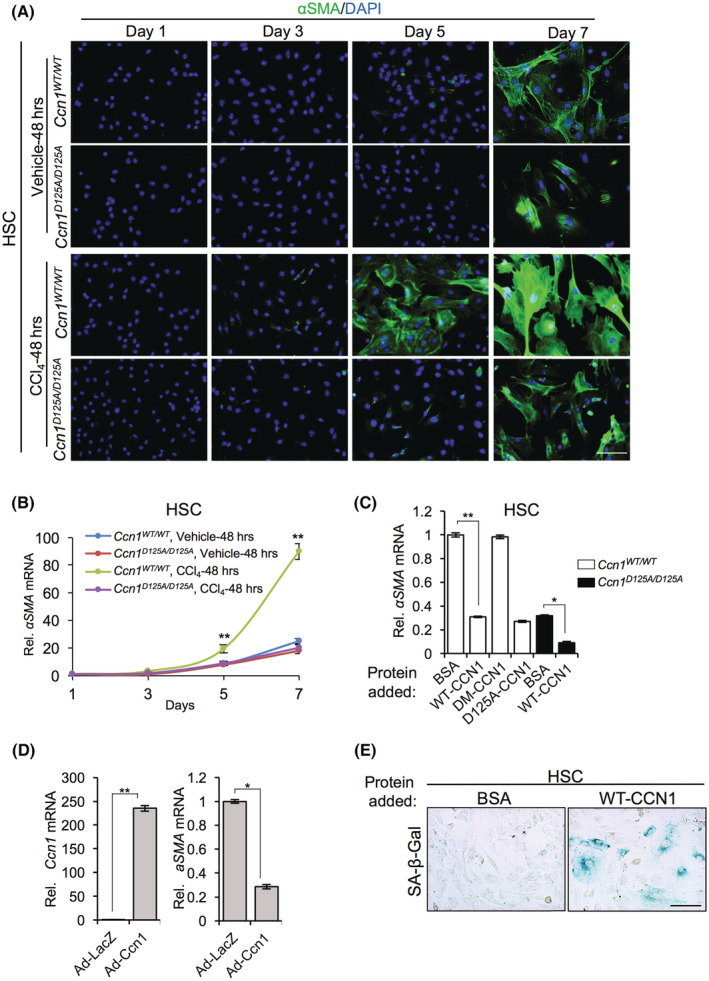
Impaired HSC activation in CCl4‐injured Ccn1 D125A/D125A mice. HSCs isolated from Ccn1 WT/WT and Ccn1 D125A/D125A mice 48 hours after injection with either vehicle or CCl4 were grown in culture. (A) HSCs were stained for αSMA at indicated times. (B) αSMA mRNAs levels were measured by qRT‐PCR. (C) HSCs were incubated with BSA, CCN1, DM‐CCN1, or D125A‐CCN1 proteins (4 μg/ml), as indicated, for 4 days, and αSMA mRNAs were measured by qRT‐PCR. (D) HSCs were transduced with control Ad‐LacZ virus or Ccn1‐overexpressing Ad‐Ccn1 virus, and Ccn1 and αSMA mRNAs were measured by qRT‐PCR after 4 days. (E) HSCs were treated with purified CCN1 protein (2.5 μg/ml) or BSA for 6 days and assayed for SA‐β‐Gal activity. Data represent means ± SD. *p < 0.033, **p < 0.002; Student t test. Scale bar,100 μm. Ad, adenovirus; BSA, bovine serum albumin; CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; CCN1, cellular communication network factor 1; DAPI, 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; LacZ, beta‐galactosidase; mRNA, messenger RNA; qRT‐PCR, quantitative reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction; Rel., relative; SA‐β‐Gal, senescence‐associated beta‐galactosidase; WT, wild type; αSMA, alpha smooth muscle actin.
