FIGURE 5.
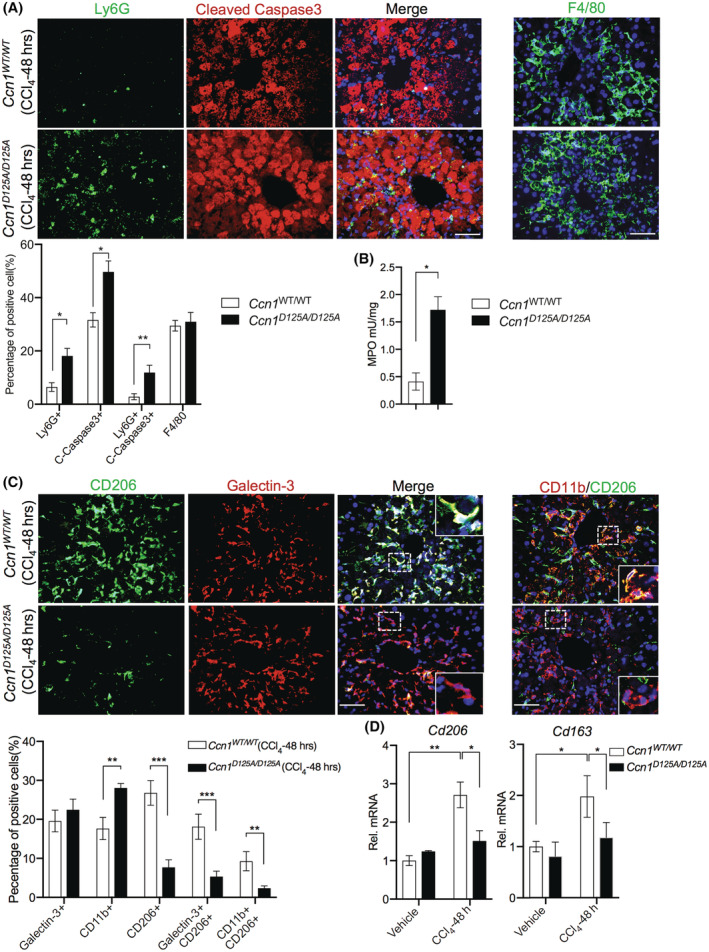
CCN1 regulates neutrophil clearance in CCl4‐induced liver injury. (A) Liver sections from Ccn1 WT/WT and Ccn1 D125A/D125A mice 48 hours after CCl4 injection were costained for Ly6G (neutrophils) and cleaved caspase 3 (apoptotic cells) as indicated and counterstained with DAPI (blue) (n = 6 each). The percentages of positive cells were quantified. (B) An MPO assay was performed with liver tissues from mice 48 hours after CCl4 injection. (C) The livers were stained for F4/80 (macrophages), and the number of F4/80‐positive cells was quantified. (D) The liver sections were also costained with CD206 and galectin‐3 or CD206 and CD11b. The percentages of positive cells were quantified. (E) The expression of cd206 and cd163 was assessed by qRT‐PCR. The percentages of positive cells were quantified and shown. Data represent means ± SD. *p < 0.033, **p < 0.002, ***p < 0.001; Student t‐test. Scale bar, 100 μm. CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; CCN1, cellular communication network factor 1; DAPI, 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; Ly6G, lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus G6D; MPO, myeloperoxidase; qRT‐PCR, quantitative reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction; Rel., relative; mRNA, messenger RNA; Tgfb1, transforming growth factor‐β1; WT, wild type.
