FIGURE 2.
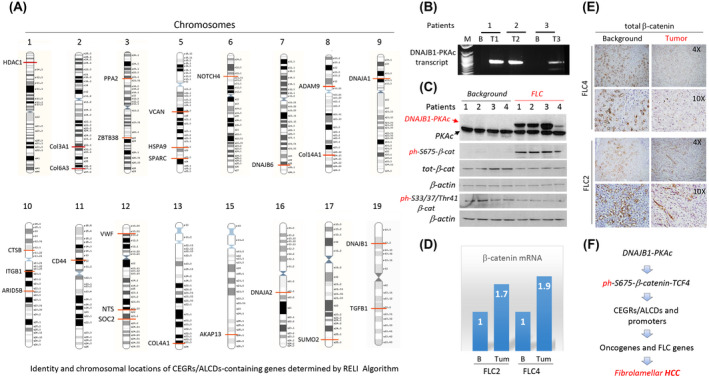
Experimental data that provide a rationale for the studies of the DNAJB1‐PKAc‐β‐catenin‐TCF4 axis as the main cause of fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma (FLC). (A) Identity of genes detected by RELI algorithm and their locations on human chromosomes. (B) Identification of the fusion DNAJB1‐PKAc transcript in patients with FLC. (C) Western blot shows expression of DNAJB1‐PKAc, total levels of β‐catenin, and levels of phosphorylated forms of β‐catenin. Antibodies (Abs) to total β‐catenin, ph‐Ser675‐β‐catenin, and ph‐Ser33/37/Thr41‐β‐catenin were used. β‐actin served as a loading control. (D) Expression of β‐catenin messenger RNA (mRNA) in patients with FLC2 and FLC4 was determined by quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). (E) Staining of background and tumor sections with Abs to total β‐catenin. (D) Hypothesis for the role of the DNAJB1‐PKAc‐ph‐S675‐β‐catenin‐TCF4‐CEGRs/ALCDs axis in FLC. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.
