FIGURE 7.
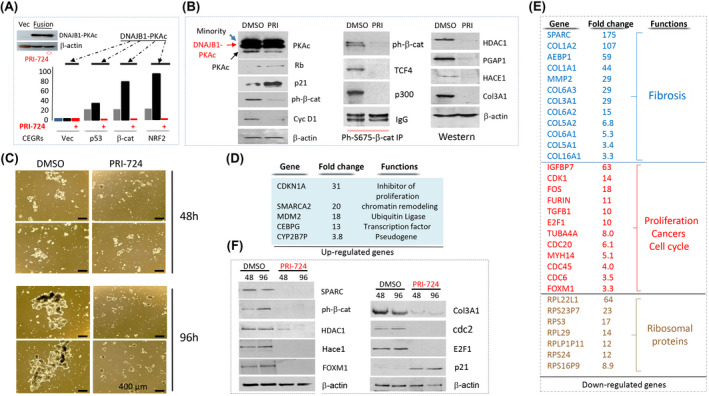
Inhibition of β‐catenin in FLC organoids reduces expression of FLC‐specific CEGR/ALCD‐containing genes and inhibits the development of FLC. (A) Western blot shows levels of DNAJB1‐PKAc in transfected cells. Bar graphs show luciferase activity of CEGR/ALCD‐luciferase constructs with CEGRs/ALCDs from p53, β‐catenin, and NRF2 genes in untreated cells, and in cells transfected with DNAJB1‐PKAc, untreated and treated with the inhibitor of β‐catenin PRI‐724 (5 μm). (B) Left: Treatment of FLC organoids with PRI‐724 (5 μm) for 24 h inhibits cyclin D1 and β‐catenin, but elevates p21 and Rb. Co‐IP study shows that PRI‐724 destroys β‐catenin‐TCF4‐p300 complexes in FLC organoids. Images on the right show levels of proteins, the genes of which contain CEGRs/ALCDs. (C) Treatment of FLC organoids with PRI‐724 (5 μm) for 96 h inhibits the proliferation of organoids and the formation of organoid structures. (D) List of top up‐regulated mRNAs that were determined by RNA‐seq in FLC organoids after treatments with PRI‐724 for 96 h (5 μm, n = 4/group). (E) List of genes reduced in FLC organoids with inhibited β‐catenin activity. (F) Western blot confirms changes of expression of proteins, the mRNAs of which were found by RNA‐seq.
