FIGURE 3.
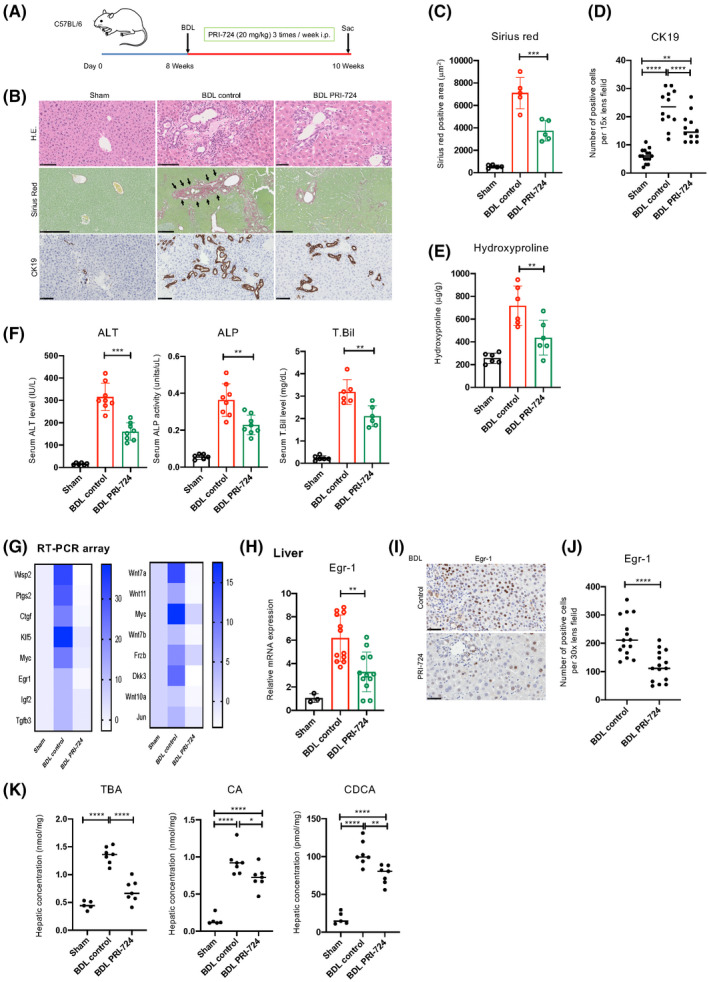
PRI‐724 suppresses liver injury and fibrosis accompanied by reduced hepatic and serum BA levels. Male wild‐type C57BL/6 male 8–10‐week‐old mice were subjected to bile duct ligation (BDL) or sham operation and treated with PRI‐724 (20 mg/kg, 3 times a week) or phosphate‐buffered saline (PBS). The animals were killed on day 14 after surgery. (A) Scheme of the treatment protocol. (B–D) HE, sirius red staining, and immunohistochemical staining for CK19 (B; scale bars, 100, 500, and 250 μm, respectively, from the top figure). Quantification of the sirius red–positive area (C) and CK19‐positive cells (D). (E) Collagen deposition as assessed by measuring hydroxyproline contents. (F) Serum ALT, ALP, and T.Bil levels. (G) Clustergrams of PCR array analyses of WNT/β‐catenin‐related genes (left panel, WNT/β‐catenin signals; right panel, WNT/β‐catenin targets). (H) Egr‐1 mRNA expression in the livers as determined by real‐time quantitative PCR (n = 3–12 per group). (I) Immunohistochemical staining using anti‐Egr‐1 antibodies (scale bar, 50 μm). (J) Quantification of Egr‐1‐positive cells in the livers. (K) Hepatic TBA, CA, and CDCA levels (n = 6–9 per group). The results shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data represent mean ± SD; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005, and ****p < 0.0001 by one‐way ANOVA (C–F,H,K) or unpaired Student's t test (J).
