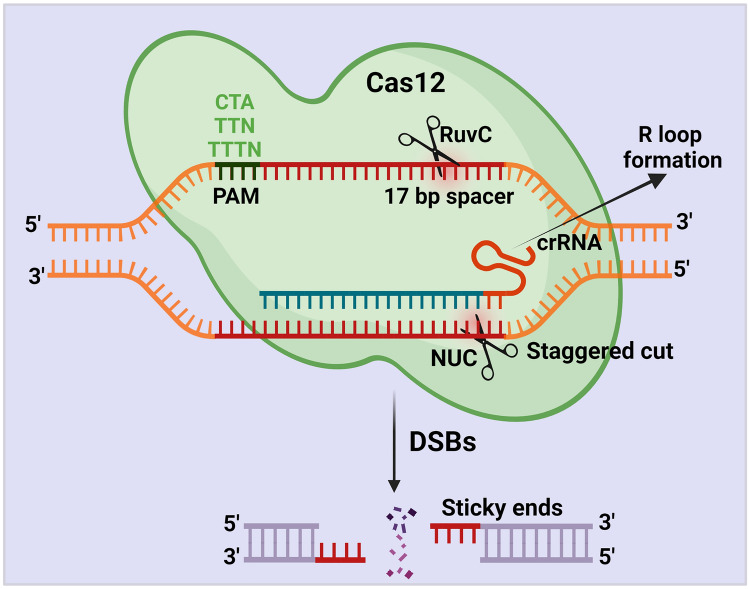
Fig. 4.
Schematic illustration of CRISPR/Cas12 mechanism. The Cas12 protein requires only the crRNAs to generate DSBs. Cas12 protein cleaves the target region beside a PAM sequence (CTA, TTN, TTTN) with the help of the RuvC and nuclease lobe (NUC) domains. Once Cas12 starts encountering, it initiates R-loop, which forms base-pair hybridization between the crRNA and the target DNA strand. During this step, Cas12 matches the < 17 bp of the target sequence and leads to an R-loop formation. Once R-loop is formed, the Cas12 protein uses its active RuvC domain and generates a staggering cut in the non-target strand with the help of the PAM sequence