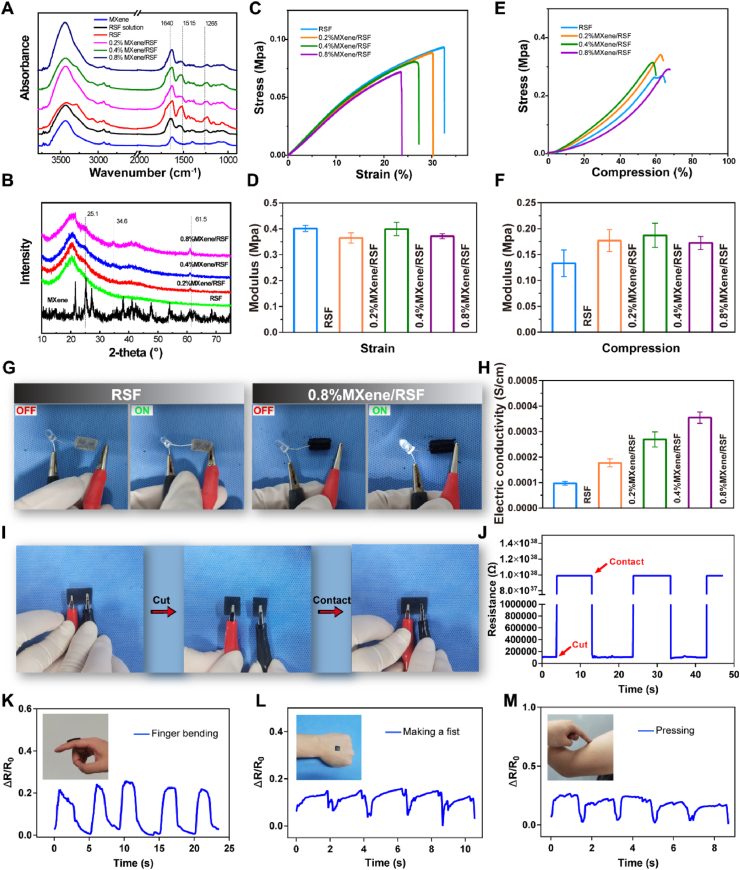
Fig. 3.
Chemical structure and multifunctional properties of the MXene/RSF hydrogel. (A) FT-IR spectra of the RSF solution, MXene nanosheets, and RSF-based hydrogel samples. (B) XRD patterns of the different hydrogel samples. (C, D) Tensile stress–strain curves and elastic moduli for the different hydrogel samples. (E, F) Compressive stress–compression curves and compression moduli for the different hydrogel samples. (G) Electrically conductive pathways made of RSF and MXene/RSF hydrogels to illuminate an LED. (H) Electrical conductivity of hydrogels with various concentrations of MXene. (I, J) Cut-contact tests for the MXene/RSF hydrogel using a real-time resistance response. (K–M) Sensors assembled from MXene/RSF to monitor various human movements including finger bending, fisting, and pressing.