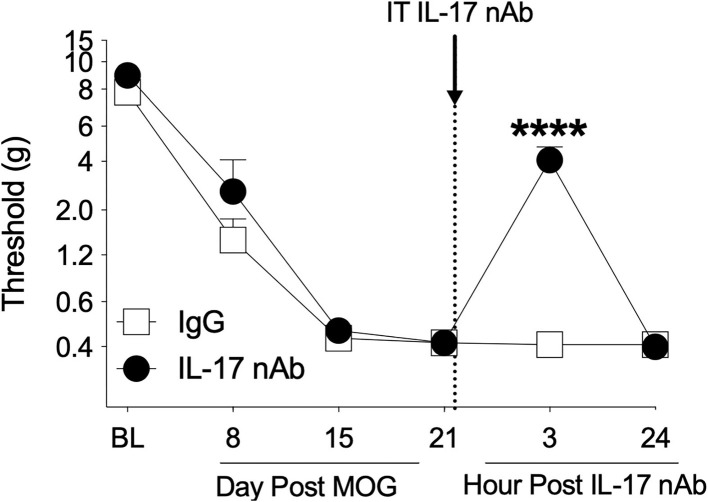
Figure 6.
Intrathecal administration of interleukin-17 neutralizing antibodies (IL-17 nAb) reverses EAE-related pain in Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats. Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were baselined (BL) for mechanical withdrawal thresholds via the von Frey test, followed by intradermal low-dose (8 μg) myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG). Approximately 4 μg of Interleukin-17 neutralizing antibodies (IL-17 nAb) or IgG control was intrathecally administered (see dotted line/arrow indicating time of drug delivery), and allodynia was assessed prior to and at 3 and 24 h post-IL-17 nAb delivery. Intrathecal administration of IL-17 nAb reversed EAE-induced mechanical allodynia at 3 h but not 24 h post-administration. Main effects of day [F(5, 70) = 142.5; p < 0.0001], IL-17 nAb [F(1, 14) = 19.57; p < 0.001], and interaction between day and IL-17 nAb [F(5, 70) = 17.48; p < 0.001]. N = 8/group. Post-hocs: **** indicates significant differences between saline control and each dose of IL-17 nAb.