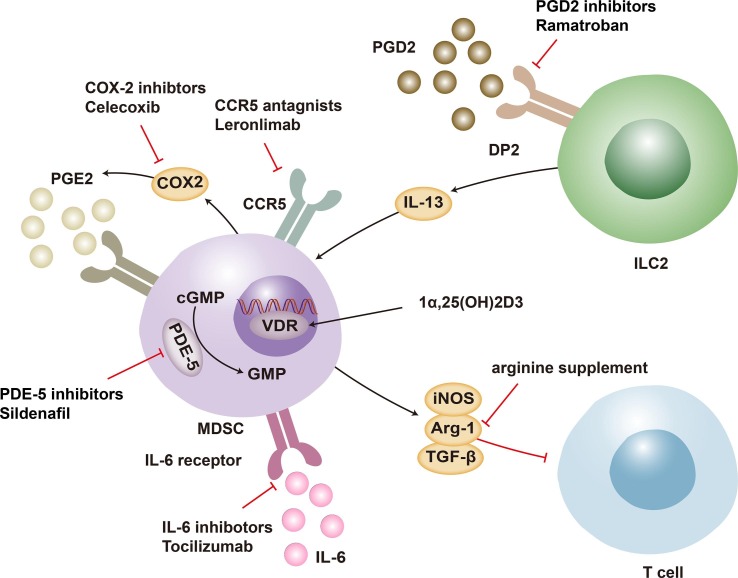
Fig. 2.
Strategies for targeting MDSCs. The therapeutic approaches that target the proliferation, differentiation, and reprogramming of MDSCs may assist in the recovery from lymphopenia in COVID-19 patients. MDSC-induced lymphopenia is mediated by PGE2 generated from arachidonic acid through COX-2 catalysis. MDSCs express COX-2, which contributes to their own immunosuppressive function. Inhibitors of COX-2 interrupt this positive feedback loop. 1,25(OH)2D3 penetrates cells and binds to VDR, hence inhibiting MDSC activation. The PDEs catalyze the hydrolysis of cGMP. PDE-5 drugs that enhance cGMP limit the production of iNOS and Arg-1, leading to reducing MDSC-mediated T-cell suppression. CCR5 inhibitors reduce the recruitment of MDSCs, hence impeding their interaction with lymphocytes. As an immunotherapy for lymphopenia, a PGD2 receptor antagonist of PGD2/DP2 signaling is suggested, given that PGD2 is essential for MDSC overexpression through DP2 receptor signaling. It has been hypothesized that l-arginine inhibits the immunosuppressive activity of MDSCs. Moreover, IL-6 receptor inhibitors may improve HLA-DR expression and decrease M−MDSC synthesis in plasma. MDSC: myeloid-derived suppressor cell; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; VDR: vitamin D receptor; cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate; PDE: phosphodiesterase; iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase; Arg-1: arginase 1; PGD2: prostaglandin D2; DP2: d-type prostanoid receptor 2; IL-6: interleukin-6; ILC2: innate lymphoid cells.