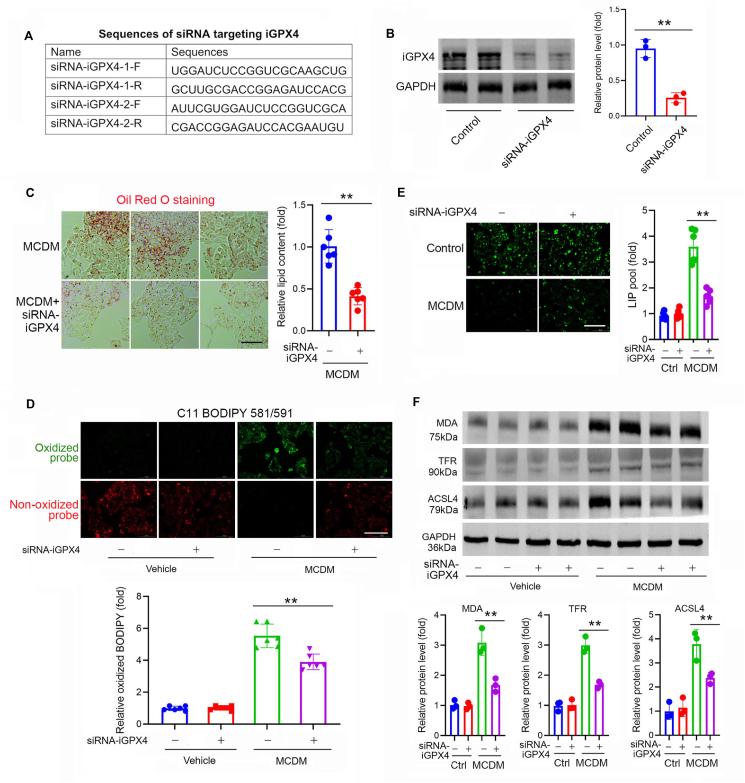
Figure 7.
Knockdown of iGPX4 isoform alleviates ferroptosis and lipid oxidation in an in vitro MAFLD model. (A) Oligonucleotide sequence of siRNAs targeting to iGPX4. (B) Efficiency of knockdown of iGPX4 by siRNA was confirmed by immunoblotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control (n = 3 per group). (C) Oil Red O staining showing the lipid content (red) induced by MCDM was largely prevented by knocking down of iGPX4 with siRNA (n = 6 per group). Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) Staining of with C11 BODIPY 581/591 probe showing the lipid oxidation (green) induced by MCDM was largely attenuated by knocking down of iGPX4 with siRNA (n = 6 per group). Scale bar, 100 μm. (E) Staining of with Calcein-AM probe, a fluorescein-derived dye with green fluorescence that is quenched upon binding to ferrous ion (Fe2+) showing the intracellular labile iron pool (LIP) induced by MCDM was prevented by knocking down of iGPX4 with siRNA (n = 6 per group). Scale bar, 100 μm. (F) Immunoblotting showing the levels of MDA, TFR and ACSL4 induced by MCDM were attenuated by knocking down of iGPX4 with siRNA (n = 3 per group). Data are presented as mean ± SEM, one way-ANOVA was performed; ∗∗P < 0.01 vs. MCDM.