Figure 3. Functional mapping of targeting dependencies for matrix proteins reveals multiple non‐canonical Pex5 substrates.
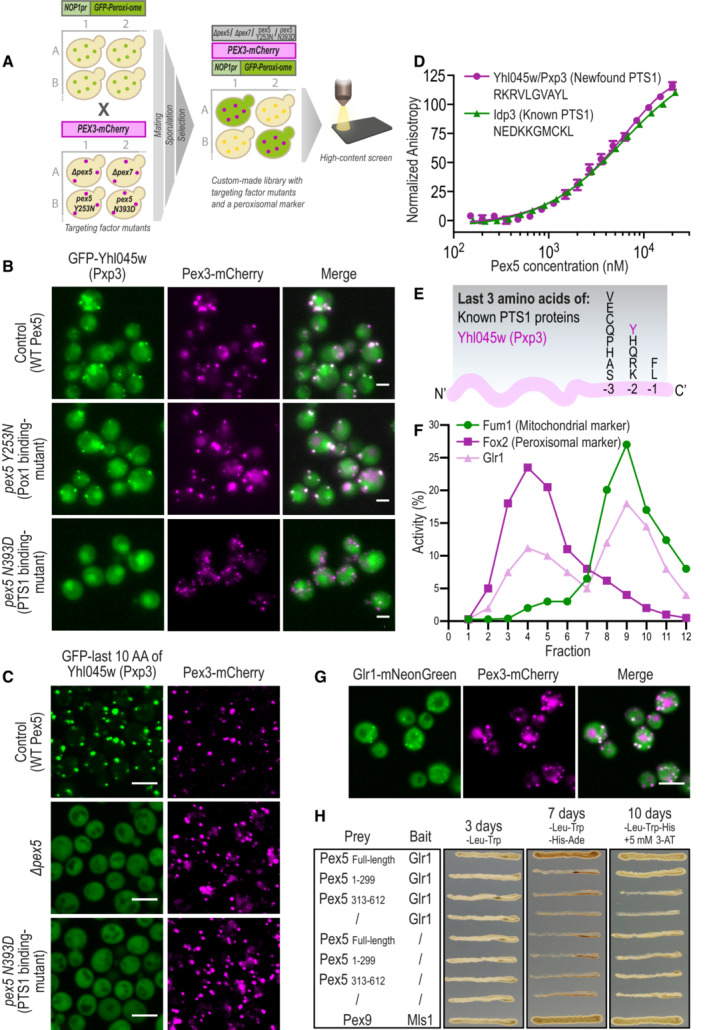
- Targeting dependencies of the newly identified peroxisomal matrix proteins were uncovered using a high‐content screen. Targeting factor deletions (∆pex5 or ∆pex7) or point mutations (PEX5 Y253N weakens the interaction with Pox1, a non‐PTS1 protein, and PEX5 N393D weakens the interaction with PTS1 proteins), were used to examine the effects on peroxisomal localization of each newly identified protein. A strain carrying a Hygromycin selection cassette in an inert locus was used as a control for no modification in peroxisomal genes.
- Matrix proteins targeting was dependent on the PTS1 pathway of the Pex5 targeting factor (full analysis in Dataset EV1). Presented is GFP‐Yhl045w, which was not targeted to peroxisomes upon a point mutation in the PTS1‐binding domain of Pex5 (PEX5 N393D).
- The peroxisomal targeting ability of the predicted motifs was examined by fusing the last 10 amino acids of each protein to the C′ of GFP, integrating the construct into an inert locus in the yeast genome, and imaging. While most motifs were unable to target GFP to peroxisomes (Appendix Fig S4B), the Yhl045w (Pxp3) motif was sufficient to target GFP to peroxisomes, in a Pex5 PTS1‐binding site‐dependent manner.
- A fluorescence anisotropy experiment demonstrated direct binding of the Pxp3 motif with purified Pex5 protein (Kd = 9.5 ± 2.9 μM), in strength similar to the binding of the known PTS1 motif from Idp3 (Kd = 5.5 ± 0.5 μM). The plots represent the mean of three independent experiments, and the error bars represent the standard deviation.
- The consensus sequence of PTS1 motifs in yeast is now extended with the newly identified, unique, residue (Tyrosine, Y) at position −2 of Pxp3.
- Subcellular fractionations followed by enzymatic activity assays show that untagged, native, Glr1 is active in peroxisomes, in addition to its known activity in mitochondria. Fum1 and Fox2 were used as markers for mitochondrial, and peroxisomal fractions, respectively.
- Glr1 C′ was fused to mNeonGreen and its peroxisomal localization was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy, demonstrating that Glr1 does not rely on a free C′ for targeting to peroxisomes hence it does not contain a PTS1 motif.
- Yeast‐2‐hybrid assay shows Glr1 interacts in vivo with both Pex5 full‐length and Pex5 N′ domain.
Data information: For all micrographs, a single focal plane is shown. The scale bar is 5 μm.
