Figure 1. Benzodiazepine + co-administered drug pairs and associations with unintentional traumatic injury.
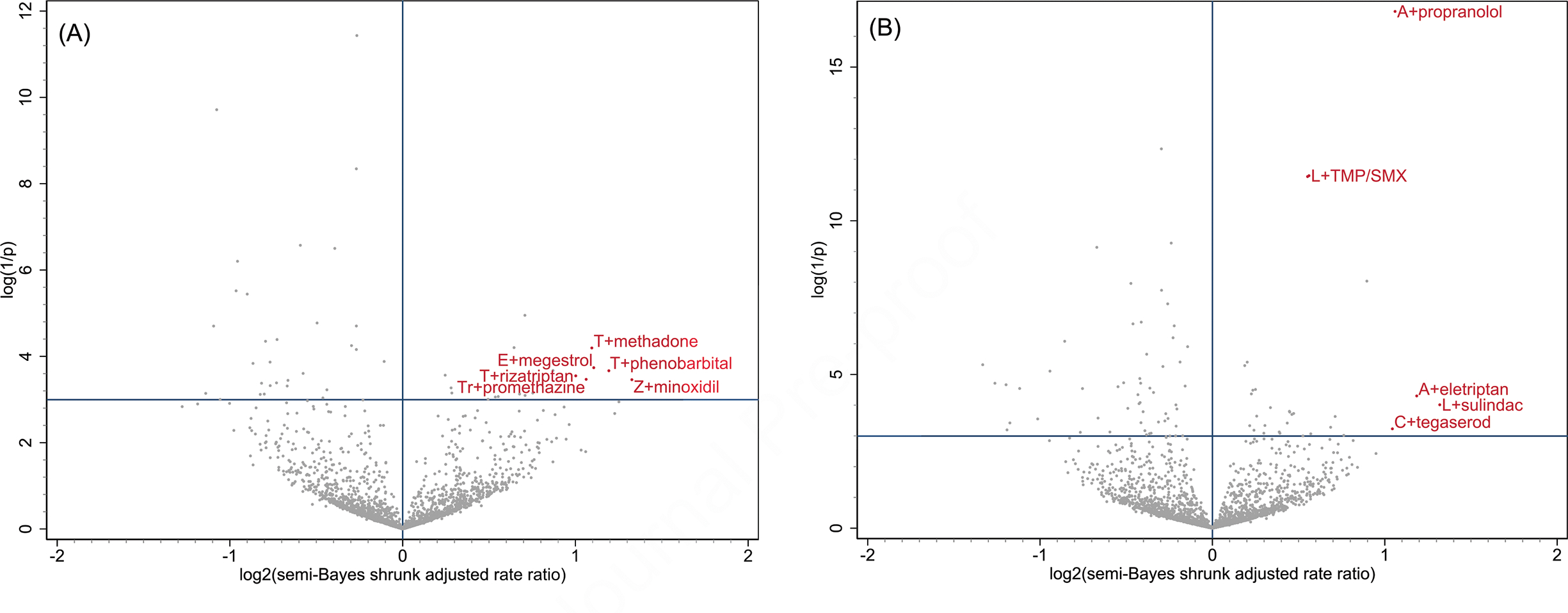
Panel (A) depicts associations for benzodiazepine and nonbenzodiazepine hypnotics: estazolam, eszopiclone [E], flurazepam, quazepam, ramelteon, suvorexant, tasimelteon, temazepam [T], triazolam [Tr], zaleplon, and zolpidem [Z]
Panel (B) depicts associations for benzodiazepine anxiolytics: alprazolam [A], chlordiazepoxide, clobazam, clonazepam [C], clorazepate, diazepam, lorazepam [L], and oxazepam
X-axes, representing the magnitude of association, are the log base 2 semi-Bayes shrunk adjusted rate ratio (RR) for benzodiazepine + co-administered drug vs. benzodiazepine alone. Y-axes, representing statistical significance, are the log (1/p-value) for the semi-Bayes shrunk adjusted RRs.
Data points in each upper right quadrant represent statistically significant elevated semi-Bayes shrunk adjusted RRs for the association between benzodiazepine + co-administered drug vs. benzodiazepine alone and unintentional traumatic injury (i.e., potential drug interaction signals). For ease of reading, we limited labeling to upper right quadrant data points with log base 2 semi-Bayes shrunk adjusted RR ≥1 or log (1/p value), for the semi-Bayes shrunk adjusted RR, ≥10. TMP/SMX: trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
