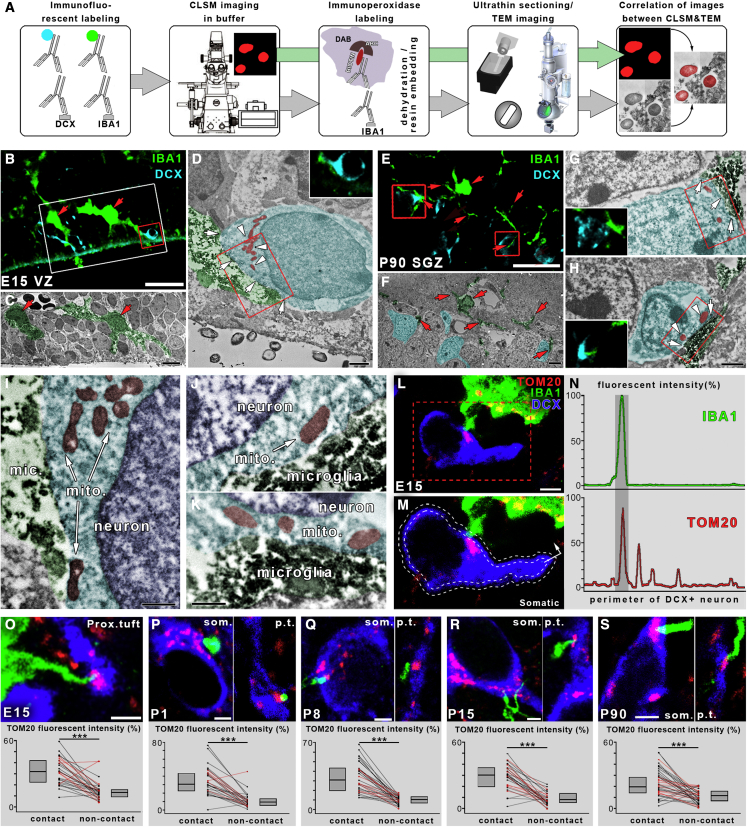
Figure 2.
Microglial processes form direct membrane-membrane contacts with the cell bodies of DCX+ developing neurons at sites enriched with mitochondria
(A) Schematic of correlated light and electron microscopy workflow.
(B–D) Maximum intensity projection of a 1.5-μm-thick volume from a CLSM stack from an E15 mouse shows an example of identified microglia-neuron somatic junctions (B). IBA1+ microglia are shown in green, DCX+ neurons are shown in cyan, the area in the white box is shown on a correlated transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image in (C), and red arrows point to corresponding microglia. The somatic junction within the red box in (B) is enlarged in the TEM image in (D). White arrows point to the direct membrane-membrane contact, and white arrowheads mark neuronal mitochondria close to the junction. The small CLSM inset shows the single confocal image plane closest to the TEM image. TEM images are pseudo-colored (microglia in green, developing neurons in cyan, and mitochondria in red). All 6 CLSM-identified contacts proved to be direct membrane-membrane contacts after TEM assessment.
(E–H) Same as (B)–(D) from a P90 mouse; the somatic junction within the left red box in (E) is enlarged in the TEM image in (G), and the junction within the right red box in (E) is enlarged in the TEM image in (H). All 10 CLSM-identified contacts proved to be direct membrane-membrane contacts after TEM assessment.
(I–K) Areas within red boxes in (D), (G), and (H), respectively, are enlarged from subsequent ultrathin sections.
(L) CLSM image showing an example of IBA1-labeled (green) microglia contacting the cell body of a DCX+ postmitotic neuron (blue) exactly where a large mitochondrion (TOM20 labeling, red) resides within the neuronal cell body. The area within the red dashed line is enlarged in (M).
(M) The process of a semi-automated unbiased analysis of fluorescence intensity area.
(N) The intensity values are plotted along the perimeter of the neuron.
(O) Example of a microglial process (green) contacting the proximal tuft of a DCX+ neuron in an E15 brain. Results show that TOM20 fluorescence intensity is significantly higher within the contact sites than outside of them. Each line represents results from one neuron; somata are represented by black and proximal tufts by red lines. Median values and interquartile range are marked by gray boxes (n = 164 cells from 3 mice).
(P–S) CLSM examples of mitochondrial enrichment at somatic (som.) and proximal tuft (p.t.) junctions in cortical brain samples from P1, P8, P15, and P90 mice and corresponding results. Images and measurements are from the cortical plate in E15 mice, neocortex from P1–P15 mice, and hippocampal dentate gyrus from P90 mice (3 mice/age group). Wilcoxon matched-pairs test; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
Scale bars represent 30 μm in (B); 4 μm in (C); 1 μm in (D), (G), and (H); 500 nm in (I)–(K); 20 μm in (E), 3 μm in (L); 2 μm in (F) and (O)–(S); this also applies to insets. See also Figures S2J–S2M and Table S2.