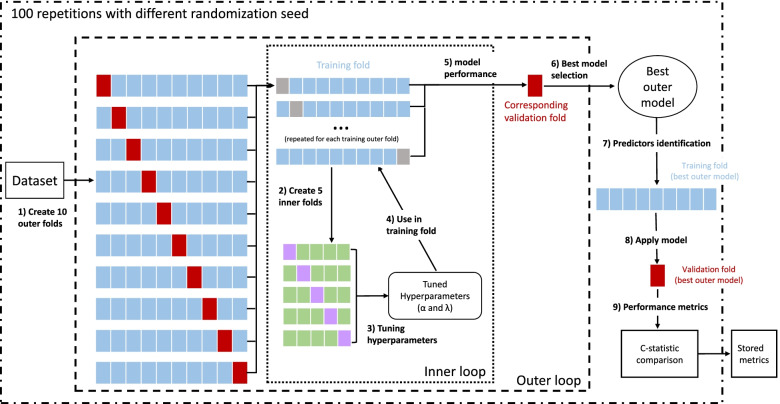
Fig. 1.
Scheme of the repeated nested cross-validation procedure. The following procedure was repeated 100 times to account for variation in results due to random partitioning of the cross-validation folds. The steps in the analyses are (1) Partition dataset into 10 outer folds with the same dementia rate in each fold. (2) Further partition each training outer fold (blue boxes) into 5 inner folds (same dementia rate) to build the inner loop. Grey boxes represent the validation folds (outer loop) which are not involved in the inner loop. 3) Use inner folds to tune the hyperparameters, select best combination of α and λ (model with the lowest partial likelihood deviance in the inner loop). (4) Apply selected hyperparameters to the corresponding training outer fold. (5) Evaluate model performance in the corresponding outer validation fold (red box). (6) Choose the best of 10 outer models (lowest partial likelihood deviance). (7) Identify predictors (variables with non-zero beta-coefficients) in the training fold of the best model in the outer fold. (8) Apply the best outer model hyperparameters to the corresponding validation outer fold. (9) Compare the c-statistic of the prediction model to the c-statistic of an age-specific model in the same validation outer fold