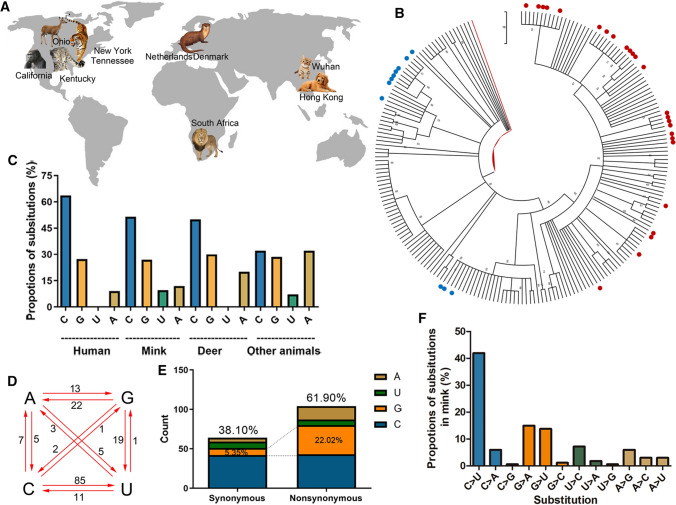
Fig. 1.
Composition and substitution analysis of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from animals. (A) The reported animals infected with SARS-CoV-2 with the defined transmission route from humans to animals. (B) Phylogenetic tree constructed by the maximum-likelihood method with the Tamura-Nei model in MEGA X with 500 bootstrap replicates. Red dots represent human sequences from infected animals, and blue dots represent sequences from infected white-tailed deer. (C) The proportions of uracil, guanine, thymine, and cytidine substitutions (nonsynonymous) in SARS-CoV-2 isolated from human or animals. (D) Base pair changes observed in the SARS-CoV-2 genomes. All of the transitions and transversions are listed in Supplementary Table S2. (E) The synonymous and nonsynonymous substitutions in mink SARS-Cov-2. (F) The relative proportion of each nucleotide substitution in the mink SARS-CoV-2 genome.