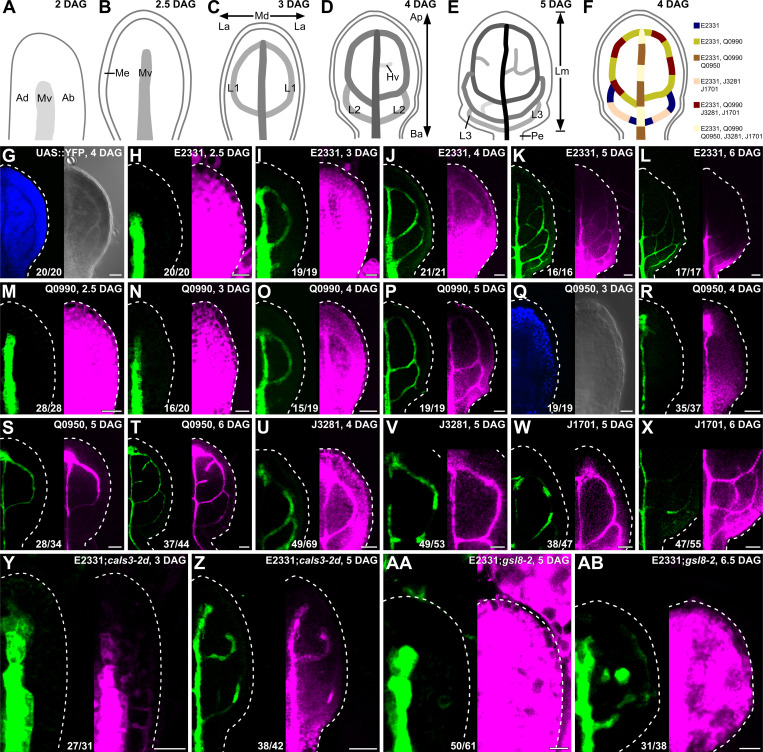
Fig 2. PD permeability changes during leaf development.
(A–F) Top right: leaf age in DAG. (A–E) Veins form sequentially during Arabidopsis leaf development: The formation of the midvein is followed by the formation of the first loops of veins (“first loops”); the formation of first loops is followed by that of second loops and minor veins; and the formation of second loops and minor veins is followed by that of third loops. Loops and minor veins form in a tip-to-base sequence during leaf development. Increasingly darker grays depict progressively later stages of vein development. Ab, abaxial; Ad, adaxial; Ap, apical; Ba, basal; Hv, minor vein; L1, L2, and L3: first, second, and third loop; La, lateral; Lm, lamina; Md, median; Me, marginal epidermis; Mv, midvein; Pe, petiole. (F) Expression map of tissue- and stage-specific GAL4/erGFP ET drivers in developing leaves illustrates inferred overlap and exclusivity of expression. (G–AB) Differential interference contrast (G, right; Q, right) or confocal laser scanning (all other panels) microscopy. First leaves (for simplicity, only half-leaves are shown). Blue, autofluorescence; green, GFP expression; magenta, YFP signals. Dashed white line delineates leaf outline. Top right: leaf age in DAG and genotype. Bottom center: reproducibility index (see S1 Table). Bars: (H, I, M, N, Q, Y, AA) 20 μm; (G, J, O, R, U) 40 μm; (K, P, S, V, W, Z, AB) 60 μm; (L, T, X) 80 μm. cals3-2d, callose synthase - 2 dominant; DAG, days after germination; erGFP, endoplasmic-reticulum-localized GFP; ET, enhancer trap; gsl8-2, glucan-synthase-like - 2; PD, plasmodesma.