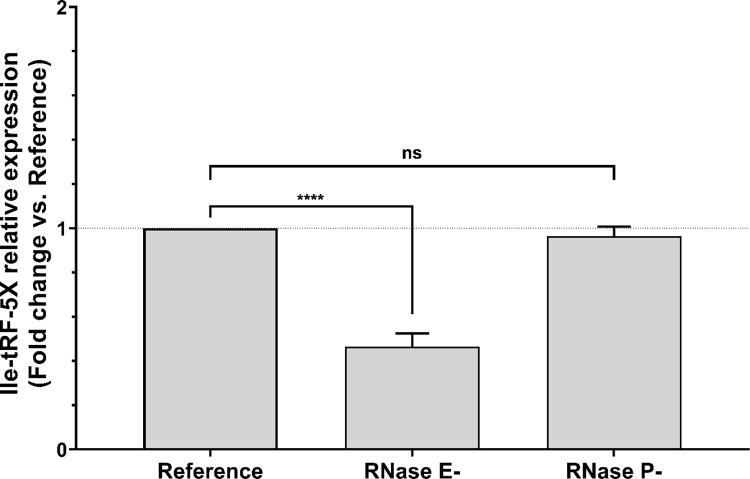
Fig 4. Bacterial RNase E contributes to Ile-tRF-5X biogenesis.
E. coli strains carrying heat-sensitive (hs) mutations in the essential genes rne-3071-hs (EM1277) and rnpA-hs (KP1036) were grown in LB medium at 30°C and then heat-shocked to transiently inhibit ribonuclease (RNase) P or RNase E, which are involved in tRNA maturation (for details, see S1 Table and S2 Fig). The level of Ile-tRF-5X was measured by LNA RT-qPCR. A spike-in (UniSp6) and reference genes (23S and/or 16S) were used as control and for normalization. The results are reported in fold change compared to the reference condition. Statistical analysis. Data were calculated from three biological replicate measurements (n = 3; mean ± SD). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Holm-Šídák’s multiple comparisons test (post-hoc test) were used for statistical analysis. Statistically significant differences (fold change vs. reference) are indicated by stars (*), * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001; ns, not significant.