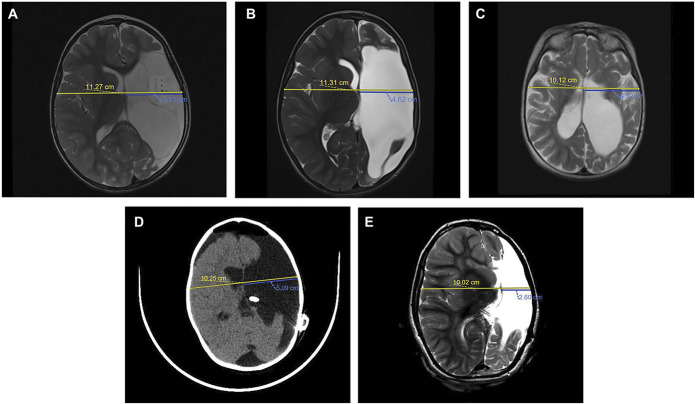
FIGURE 1.
MRI and CT scans demonstrating MLBS quantification in nonshunted and shunted patients. The biparietal diameter (yellow line) is divided by 2 and subtracted from the ipsilateral distance from the inner table to the septum pellucidum (blue line). A, Preoperative axial turbo spin echo (TES) T2-weighted MRI of the pediatric patient with history of medically intractable epilepsy secondary to left perinatal middle cerebral artery stroke demonstrating a baseline MLBS of 0.51 cm. B, Postoperative axial TSE T2-weighted MRI of the patient from A at 6 months after functional hemispherectomy demonstrating a MLBS of 1.04 cm. C, Preoperative axial TSE T2-weighted MRI of the pediatric patient with history of medically refractory infantile spasm demonstrating a baseline MLBS of 0.14 cm. D, Postoperative, noncontrast enhanced axial CT of the patient from C after functional hemispherectomy and subsequent early cerebrospinal fluid shunting secondary to PHH demonstrating a MLBS of 0.04 cm. E, Surveillance axial TSE T2-weighted MRI of the patient from C and D at a 72-month follow-up with a MLBS of 2.41 cm. CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; CT, computed tomography; MLBS, midline brain shift; TSE, turbo spin echo.