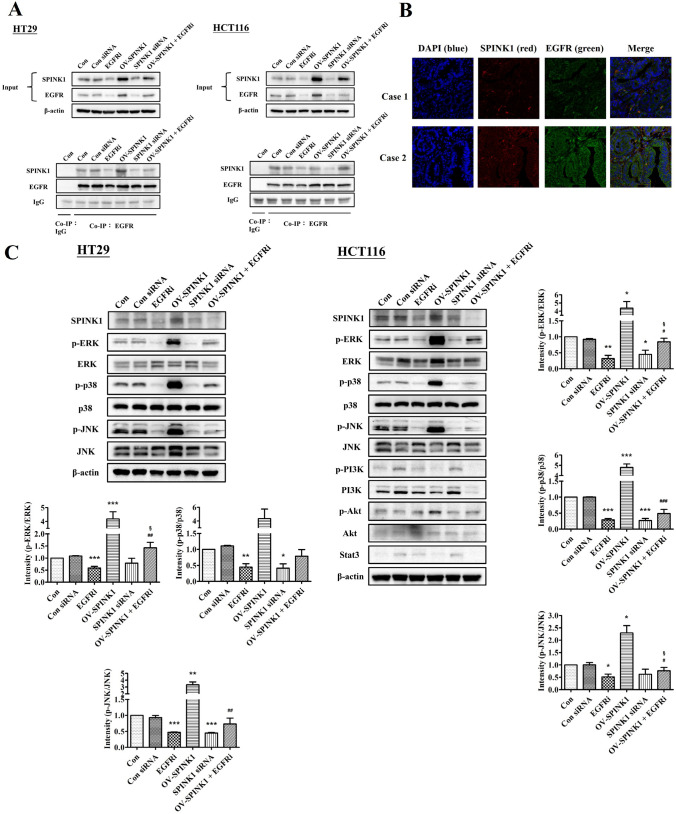
Fig. 4.
A SPINK1 directly interacts with EGFR. Cell lysates from HT-29 and HCT-116 cells treated with non-siRNA, EGFR inhibitor, p-SPINK1 and SPINK1 siRNA (with/without EGFR inhibitor) were immunoprecipitated with the EGFR antibody, followed by immunoblotting with SPINK1 antibodies. B Immunofluorescence visualization of Co-expression of SPINK1 and EGFR was observed in representative specimens of colorectal cancer patients. To visualize the cell nuclei, the cells were mounted with a DAPI-containing mounting medium (blue). SPINK1 was detected using the anti-SPINK1 antibody and a FAM-conjugated secondary antibody (red). EGFR was detected using the anti-EGFR antibody and TAMRA-conjugated secondary antibody (green). All channels merged. Objective 20x. (C) Western blot analysis for p-ERK, ERK, p-p38, p38, p-JNK, JNK and SPINK1 levels transfected with non-siRNA, EGFR inhibitor, p-SPINK1 and SPINK1 siRNA (with/without EGFR inhibitor), while a loading control β-actin was used. The quantitative data analysis was expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 as compared to the control group (n = 3/group); #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 and ###p < 0.001 as compared to the OV-SPINK1 group. §p < 0.05 as compared to the EGFRi group (n = 3/group)