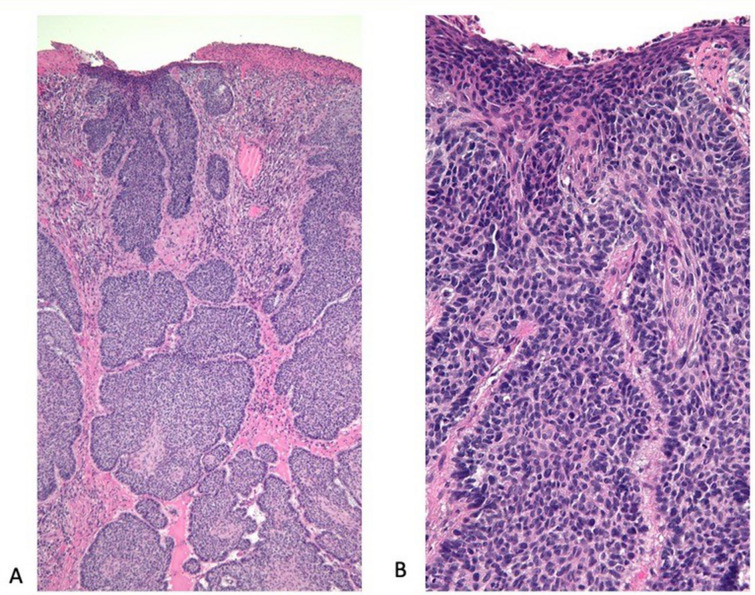
Fig. 2.
Advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC): pathology presentation. Lower (A) and higher (B) magnification views of the microscopic examination of the advanced BCC from the 62-year-old man’s left upper back show nodular aggregates of basaloid tumor cells extending from the overlying epidermis and invading the underlying dermis. Next-generation sequencing of the tumor demonstrated a high tumor mutational burden of 53 mutations per megabase (10 or more mutations per megabase is considered to be a high tumor mutational burden) and 11 deleterious genomic variants, including PTCH1 (splice site 1504-1G > T), ASXL1 Q760, INPP4B W521, KEL R130Q, PIK3R1 R534, PTEN (splice site 210 2A > T), RAC1 P29S, TERT promoter-124C > T, TP53 R196, TP53 Q100, and WT1 C350R (hematoxylin and eosin: A, × 4; B, × 20). Republished from [73] with permission from Elsevier