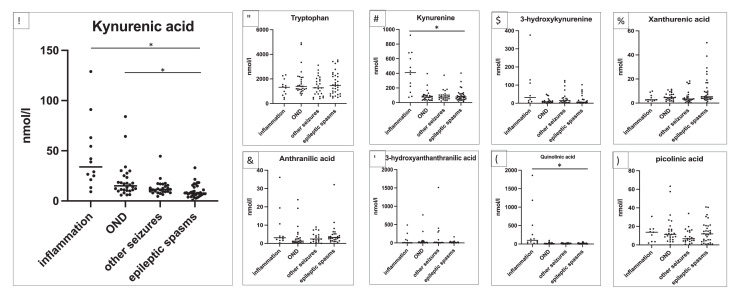
Figure 2.
Quantitative data in nmol L−1 of individual CSF patient samples for tryptophan-kynurenine metabolites in neuroinflammatory control group (n=12), other non-inflammatory neurological controls (OND, n=29), other seizures (n=26) and epileptic spasms (n=34). The primary group of interest was the epileptic spasms group, so pairwise comparisons with Mann Whitney U test were performed between the epileptic spasms group and the 3 control groups and are presented in supplementary table 6. Only statistically significant findings after Bonferroni correction are presented in the figure. Kynurenic acid was statistically significantly decreased in epileptic spasms compared to neuroinflammatory controls and OND (both p<0.0001) (Mann Whitney U test) (Figure 2a). As expected, the neuroinflammatory group had higher kynurenine (Figure 2c) and quinolinic acid (Figure 2h) compared to epileptic spasms (both p<0.0001) (Mann Whitney U test). Asterisks above the horizontal lines of the groups indicate significant difference p<0.0001.