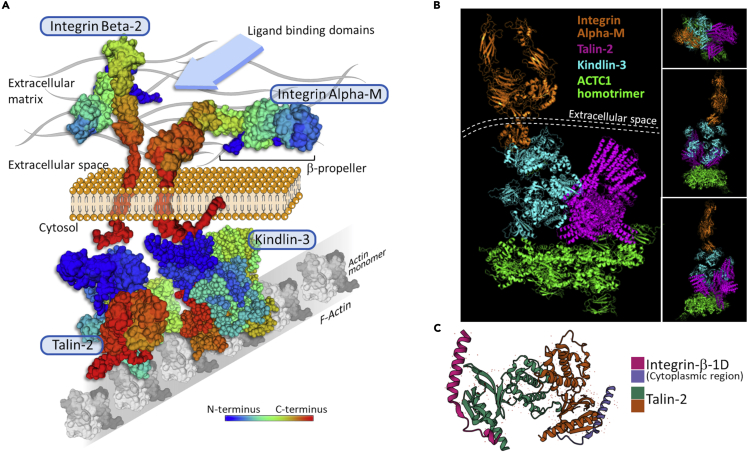
Figure 7.
Association of integrins to F-actin through talin-2 and kindlin-3 in granulocytes
(A) Hypothetical surface model of human integrins CD18 and CD11b associated with F-actin through focal adhesion molecules (Talin-2, Kindlin-3) as an early signal for integrin/ligand stabilization and clusterization within the granulocyte cell membrane. Talin-2 markedly activates Integrin-beta-2 thus increasing the affinity binding of the CD18/CD11b integrins to its ligand on cancer cells (cyan arrow). Actin (ACTC1) monomers (Uniprot code, P68032); talin-2 (Uniprot code, Q9Y4G6); kindlin-3 (Uniprot code, Q86UX7); integrin beta-2 (Uniprot code, P05107); integrin alpha-M (Uniprot code, P11215).
(B) 3D stereoscopic computational model showing integrin Alpha-M (RCSB-PDB code: 7P2D) with its C-terminal sequence (cytoplasmic region in panel A) binding the kindlin-3 (RCSB-PDB code: 7C3M) and talin-2 (RCSB-PDB code: 6R9T). These two focal adhesion molecules are in turn stably complexed to an actin homotrimer composed of ACTC1 monomers (RCSB-PDB code: 7LRG). Dashed lines represent the cell membrane separating the extracellular space from the cell cytosol. Upper right box depicts the integrin side view of the model referred to as the actin homotrimer axis. The intermediate and lower right boxes represent the kindlin-3 and talin-2 side views of the model referred to as the same trimer axis. The docking model was obtained via ClusPro processing of the indicated RCSB-PDB codes (© Kozakov et al., 2017).
(C) Particular of the integrin-talin association mediated by the cytoplasmic regions of the integrin molecule (pink & purple colors) demonstrating the ability of talin-2 to act as a focal adhesion factor by binding to integrins (RCSB-PDB code: 3G9W).