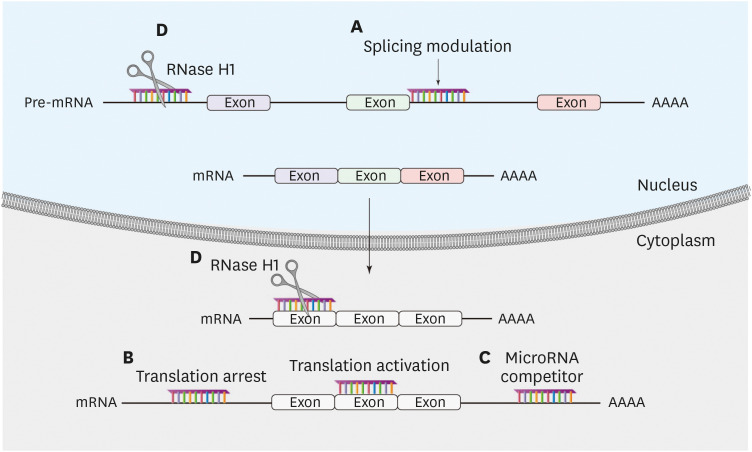
Fig. 1. Modulation of gene expression by ASOs. ASOs can modulate gene expression by two different mechanisms. First, ASOs bind and occupy the target mRNA without triggering RNA degradation (occupancy-only mediated): (A) splicing modulation by base pairing with sequence elements in pre-mRNA to inhibit or enhance the utilization of splicing sites; (B) translation modulation by base pairing with mRNA, either to inhibit or activate translation through binding to inhibitory elements; (C) microRNA modulation either by base pairing with microRNA to inhibit the function of the microRNA or by base pairing with microRNA-binding sites of a particular mRNA to eliminate the effect of a particular microRNA. Second, ASOs induce target mRNA degradation (enzymatic RNA degradation): (D) DNA-like ASOs that trigger complementary RNA cleavage by RNase H1.
ASO, antisense oligonucleotide.