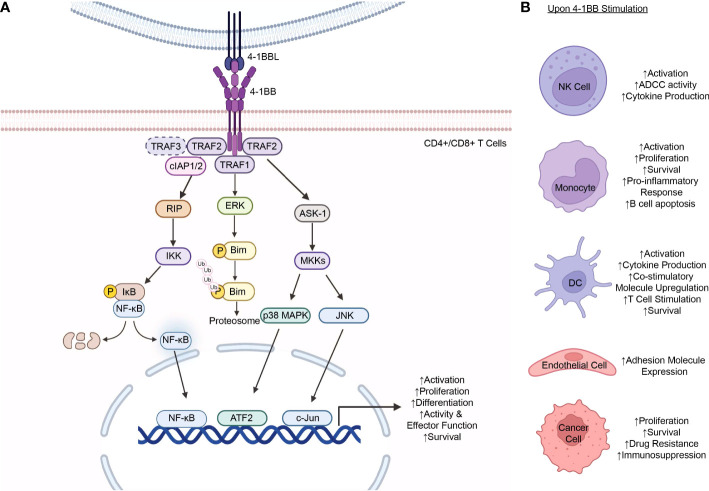
Figure 1.
4-1BB Expression and Signaling. (A) 4-1BB stimulation on T cells results in the activation of multiple signaling pathways downstream the receptor. Upon interaction with 4-1BBL and subsequent activation, 4-1BB signaling is initially mediated by the recruitment of TRAF1, TRAF2, or, hypothetically, TRAF3 (in dashed lines), to the TRAF-binding motif located in the 4-1BB cytoplasmic tail. The TRAF proteins form a homo- or hetero-trimer and, in turn, recruits cIAP1/2 which further mediates the activation of downstream effectors that transduce signals down various signaling cascades to the nucleus including the NF-κB, ERK, p38 MAPK, and JNK pathways. Signaling down these pathways results in the increased expression of the anti-apoptotic proteins, Bfl-1 and Bcl-xL, decreased expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Bim, and increased proliferation, differentiation, effector functions, and survival of the T cells. (B) 4-1BB expression is observed in a wide range of cells including NK cells (4, 35), monocytes (36–38), DCs (11, 39, 40), endothelial cells (14, 41), and malignant cancer cells (16, 42–44). Stimulation of 4-1BB on the respective cells result in varying cellular responses depending on the cell type. TRAF, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor; cIAP, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein; RIP, receptor interacting protein; IKK, IκB kinase; IκB, inhibitor of NF- κB; NF- κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; ERK, Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase; Bim, Bcl-2-like protein 11; ASK-1, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; MKK, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinases; JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; ATF2, activating transcription factor 2; P, phosphate; Ub, ubiquitin; NK cell, natural killer cell; ADCC, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; DC, dendritic cell; Bfl-1, Bcl-2-related protein A1; Bcl-xL, B cell lymphoma-extra large. The figure was created with BioRender.com.