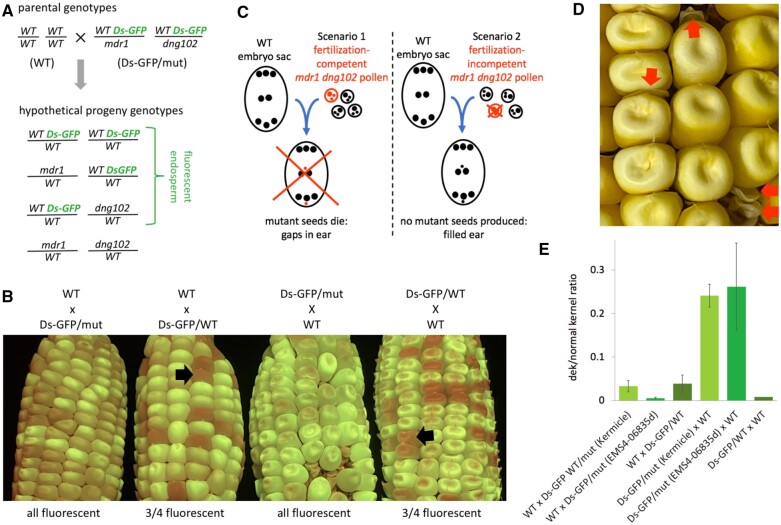
Figure 2.
A, Schematic depiction of method to quantify transmission of mdr1 and dng102 mutant alleles using Ds-GFP insertions linked to the wild-type alleles. B, Example outcomes of crosses using Ds-GFP insertions. Ds-GFP/mut is the double heterozygous mutant of mdr1 and dng102 with the wild-type alleles linked to Ds-GFP insertions. Ds-GFP/WT is homozygous wild-type for both Mdr1 and Dng102, but still heterozygous for the two Ds-GFP insertions. Black arrows indicate example nonfluorescent kernels. Fluorescence intensity depends in part on Ds-GFP dosage, from zero to four copies in triploid endosperm with insertions segregating at two loci. C, Schematic depiction of how well-filled ears indicate a pre-fertilization pollen defect. D, Defective kernel (dek) phenotype in seeds derived from a double heterozygous mutant mother plant crossed with wild-type pollen. E, Quantification of dek-like phenotype in the same crosses used to quantify Ds-GFP transmission. Error bars are standard errors of the means for each ear resulting from the crosses, except Ds-GFP/WT x WT, which was a single ear.