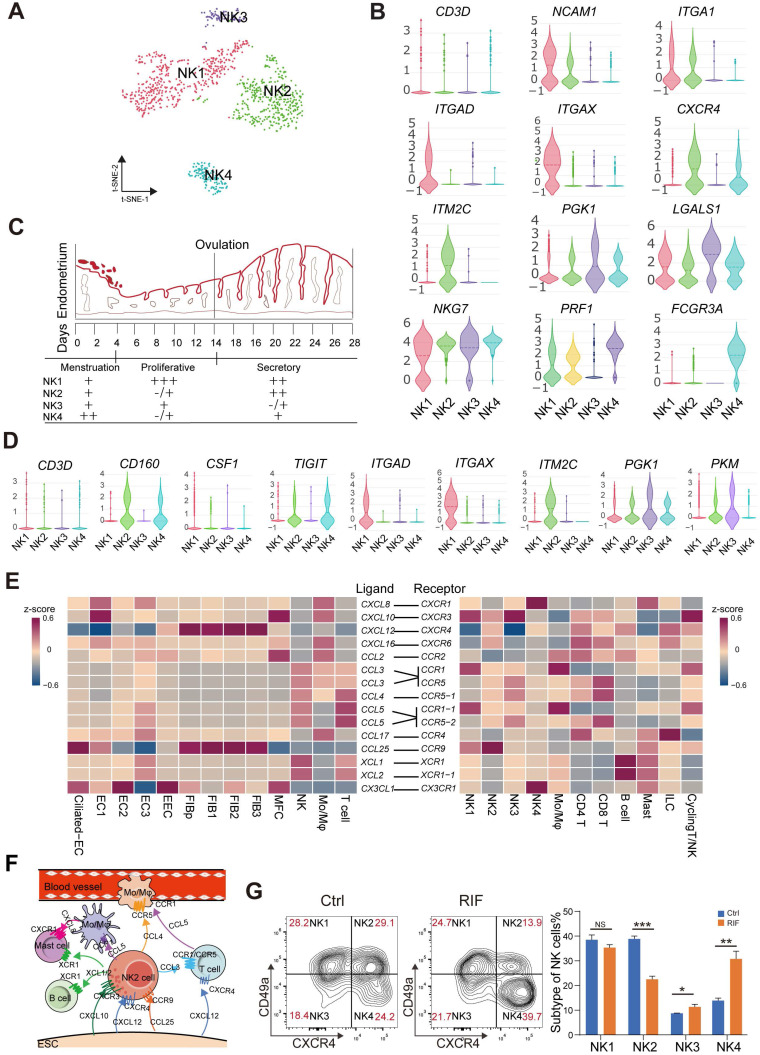
Figure 6.
Endometrial CD49a+CXCR4+ NK2 cells are decreased in the RIF patients. (A) t-SNE map of four sub-clusters of endometrial NK cells. (B) Expression of representative marker genes in Violin plots. (C) Changes of NK1, NK2, NK3, and NK4 cellular proportion in total endometrial CD45+CD3-CD56+ NK cells across the menstrual cycles were analyzed using FCM analysis (-/+: < 10%, +: < 20%, ++: < 50%, +++: ≥ 50%). (D) Expression of representative marker genes in the Violin plots. (E) Heat map of CellPhoneDB showing selected significant ligand-receptor interactions (P value < 0.05, permutation test, see Methods) between all subtypes of endometrium cells (left) and all immunocytes (right). Assays were carried out at the mRNA level, but are extrapolated as protein interactions. (F) Diagram of the main chemokine and receptors expressed on the FIBs and immunocytes that are involved in cell migration and recruitment. (G) Proportions of the four NK cellular subtypes in the endometrial stroma in the controls and RIF patients (n = 6, for each group) were analyzed by flow cytometry. Cells were initially gated within CD45+CD3-CD56+ gate, and then CXCR4 and CD49a gating. Data were presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed by t test (NS, no significance, *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001).