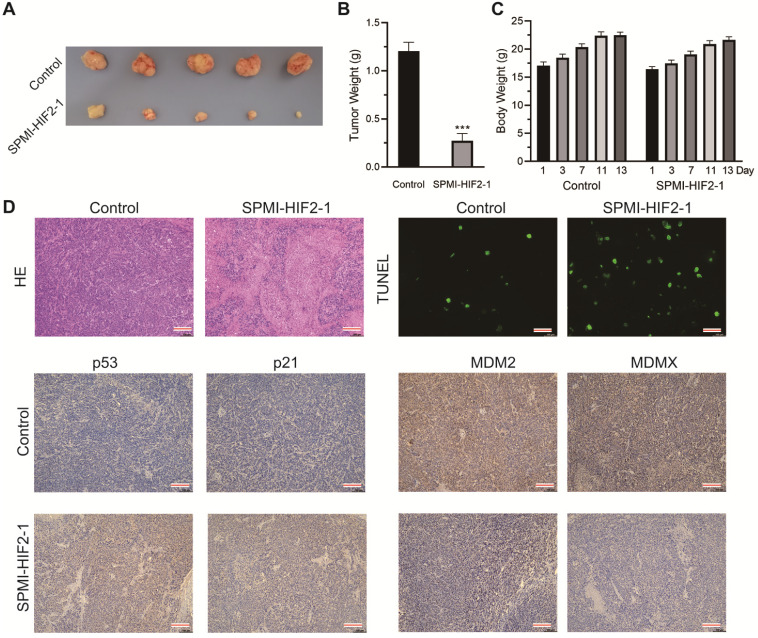
Figure 7.
SPMI-HIF2-1 inhibited tumor progression in a nude mouse CRC xenograft model. CRC xenograft models were established through orthotopical implantation of HCT116 cells into the rectal mucosa of mice. Mice were then randomly divided into two groups (n = 5 mice/group) and treated with PBS or SPMI-HIF2-1 (2 mg/kg) via tail vein injection every 2 days until the 13th day. (A) Representative images of the tumors excised at the end of the experiment. (B) Tumor weight was measured after the mice were sacrificed. P-values were calculated using the t-test (***P < 0.001). (C) Body weights of the mice were recorded at the indicated days. Data for tumor weight and body weight are shown as the mean ± SD. (D) Representative HE, TUNEL, and IHC images for p53, p21, MDM2, and MDMX in tumor sections. Significant apoptotic activity, increased p53 and p21 protein levels, and decreased MDM2 and MDMX protein levels were detected in the SPMI-HIF2-1 group. These results indicated that tumor inhibition was realized through the degradation of MDM2 and MDMX and subsequent p53 activation (scale bar: 150 µm).