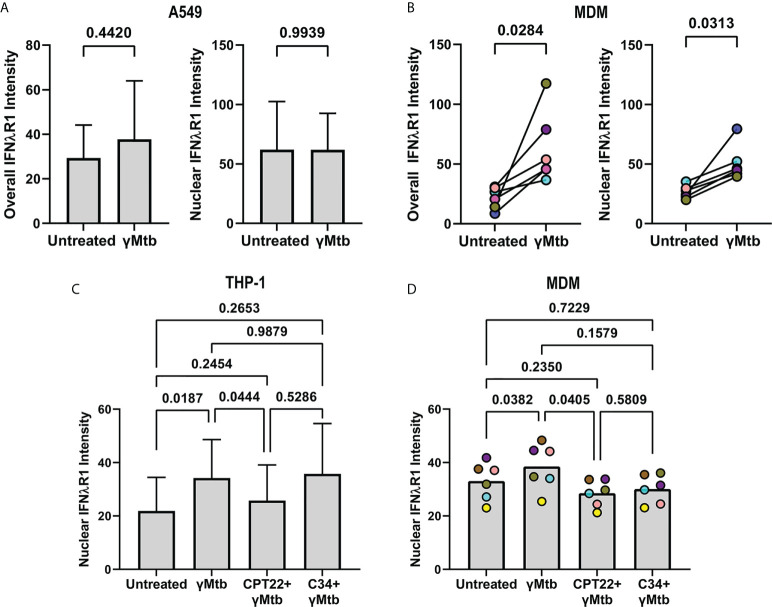
Figure 9.
TLR2 mediated signaling by gamma-irradiated Mtb regulates IFNλR1 expression and localization in myeloid cells. (A) Comparison of overall (left) and nuclear (right) IFNlR1 intensity in gamma-irradiated Mtb-stimulated A549 epithelial cells. Bars and lines represent the mean value and standard deviation from 5 independent experiments with statistical comparisons by paired t test. (B) Overall (left) and nuclear (right) IFNλR1 intensity in gamma-irradiated Mtb-stimulated macaque monocyte derived macrophages (MDMs; n=6). Each point depicts the median IFNλR1 value in macrophages, with each marker’s color representing a different animal. Statistical comparisons by Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test and paired t test, respectively. (C) Comparison of nuclear IFNλR1 intensity in gamma-irradiated Mtb stimulated THP-1 cells with or without CU CPT22 (TLR2 antagonist) and C34 (TLR4 antagonist). Bars and lines represent mean values and standard deviation of 7 independent experiments. RM one-way ANOVA used to account for repeated measures and pairwise groups compared using Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (Tukey’s adjusted p-values reported). (D) Comparison of nuclear IFNλR1 intensity in gamma-irradiated Mtb-stimulated macaque MDMs with or without CU CPT22 (TLR2 antagonist) and C34 (TLR4 antagonist) (n=6). Each point depicts the median IFNλR1 value for an animal’s MDMs, with each marker’s color representing a different animal. RM one-way ANOVA used to account for repeated measures and pairwise groups compared using Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (Tukey’s adjusted p-values reported).