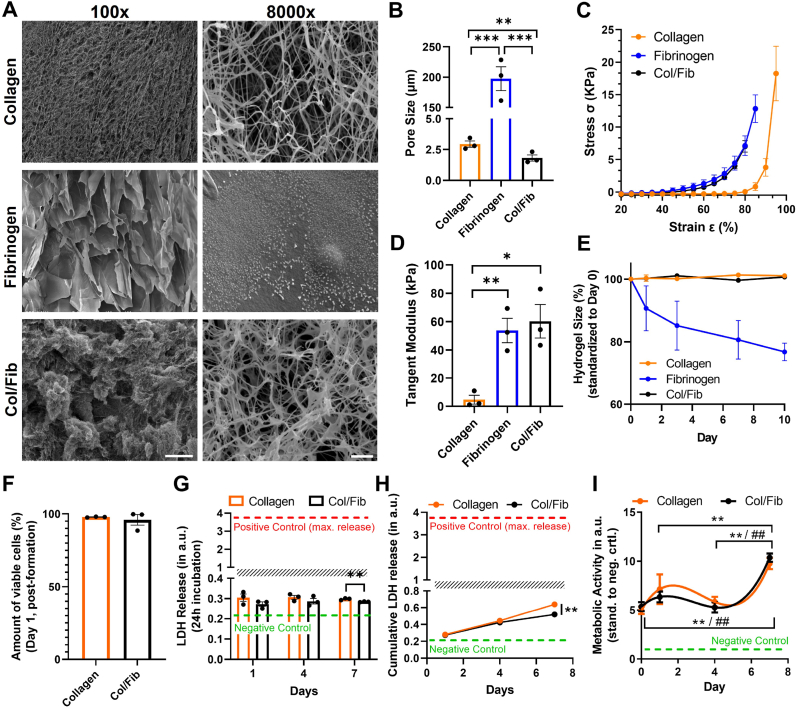
Fig. 2.
Mechanical characterization of collagen, fibrinogen and Col/Fib gels as well as PSCactivity and viability. A) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images for collagen, fibrinogen and collagen/fibrinogen (Col/Fib) hydrogel at 100x magnification, scale bar = 200 μm, and 8000x magnification, scale bar = 2 μm. B) Quantification of the average respective pore size, n = 3, 20 pores/independent sample. C) Stress – strain curve for collagen, fibrinogen and Col/Fib hydrogels based on compression analysis, n = 3. D) Tangent modulus for collagen, fibrinogen and Col/Fib hydrogels between 75% and 80% strain based on compression analysis, n = 3. E) Stability of collagen, fibrinogen and Col/Fib hydrogels based on the hydrogel size for a total duration of 10 days, n = 3. F) Quantification of viable PSCs in collagen and Col/Fib gels on day 1 post-tissue formation based on LIVE/DEAD staining (Fig. S2, Supporting Information), n = 3. G) Release of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) into culture medium based on 24 h incubation of collagen or Col/Fib gels, negative control = full culture medium, positive control = LDH released on mechanical destruction of tissues, n = 4. H) Cumulative LDH release in culture medium for collagen and Col/Fib gels for 7 days of culture, n = 3. Negative control = full culture medium, positive control = LDH released on mechanical destruction of tissues. I) Metabolic activity (based on AlamarBlue assay) of PSCs in collagen and Col/Fib gels on days 1, 4 and 7 post-preparation, n = 3. Significance indicated for * Col/Fib and # collagen. Mean + SEM, *p < 0.05, ##/**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.