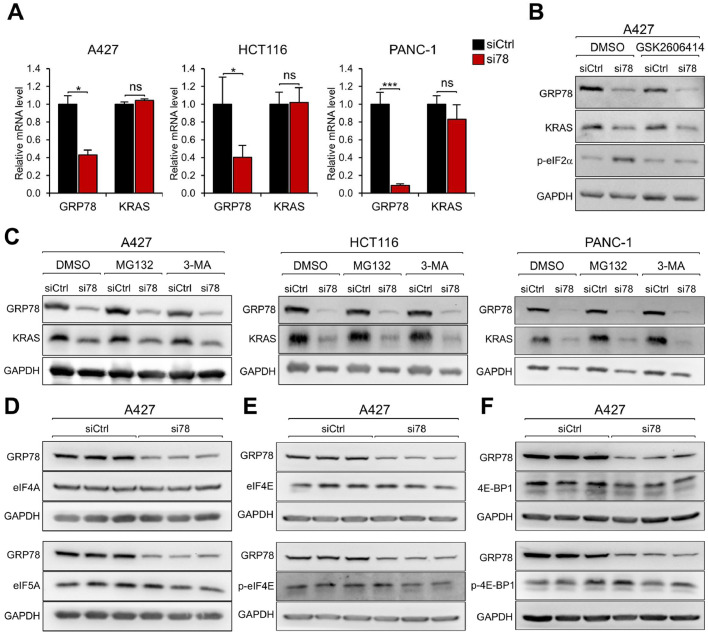
Fig. 2.
GRP78 deficiency reduces KRAS protein at the post-transcriptional level. (A) A427, HCT116, and PANC-1 cells were transfected with siCtrl or si78 for 48 hr. Total RNA was extracted and subjected to reverse transcription and real-time PCR to measure the mRNA levels of GRP78 and KRAS with GAPDH serving as control. The quantitation of the relative mRNA levels of GRP78 and KRAS after normalization against GAPDH levels is shown. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. * P ≤ 0.05, *** P ≤ 0.001, ns: not significant (Student's t test). (B) A427 cell was transfected with siCtrl or si78 for 36 hr followed by treatment of DMSO or GSK2606414 (1μM) for 12 hr. Whole cell lysate (WCL) was subjected to Western blot analysis for GRP78, KRAS, phosphorylated-eIF2α (p-eIF2α) protein levels with GAPDH serving as loading control. (C) A427, HCT116, and PANC-1 cells were transfected with siCtrl or si78 for 36 hr followed by treatment of DMSO, MG132 (10μM), or 3-MA (10mM) for 12 hr. WCL was subjected to Western blot analysis for GRP78 and KRAS protein levels with GAPDH serving as loading control. (D) A427 cells were transfected with siCtrl or si78 for 48 hr and WCL was analyzed by Western blot for GRP78, eIF4A, and eIF5A protein levels with GAPDH serving as loading control. (E) Same as in (D) except eIF4E and phosphorylated eIF4E (p-eIF4E) protein levels were analyzed. (F) Same as in (D) except 4E-BP1 and phosphorylated 4E-BP1 (p-4E-BP1) protein levels were analyzed.