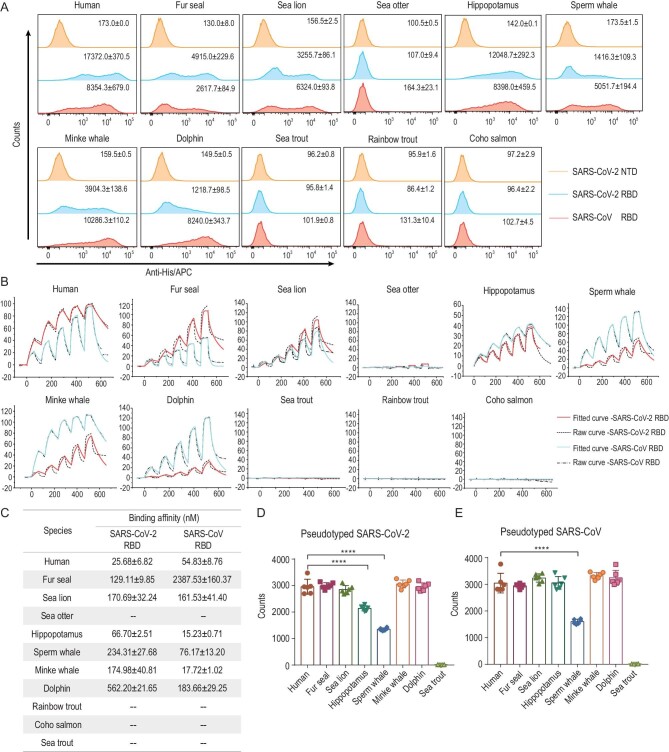
Figure 1.
Binding between ACE2s and SARS-CoV-2 or SARS-CoV RBD, and the transduction of pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 or pseudotyped SARS-CoV into BHK-21 cells expressing the relevant ACE2s. (A) His-tagged SARS-CoV-2 RBD, SARS-CoV RBD or SARS-CoV-2 N-terminal domain (NTD) proteins were incubated with BHK-21 cells expressing EGFP-tagged ACE2s, respectively. Anti-His/APC antibodies were used to detect the His-tagged protein binding to the cells. Cells stained with the SARS-CoV-2 RBD, the SARS-CoV RBD and the SARS-CoV-2 NTD proteins are shown in bright blue, pink and brown, respectively. The mean fluorescence values of APC are presented. The SARS-CoV-2 NTD was used as the negative control. (B) The mFc-tagged ACE2s in the supernatants were captured by anti-mIgG Fc antibodies immobilized on the CM5 chip, and their binding was sequentially tested with serially diluted SARS-CoV-2 RBD or SARS-CoV RBD. The raw and fitted curves are displayed in dotted and solid lines, respectively. (C) The binding affinities between ACE2s and SARS-CoV-2 RBD or SARS-CoV RBD are shown as the means ± SD of three independent experiments. (D and E) Transduction of the pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV on BHK-21 cells expressing the respective mammal ACE2 or hACE2. Error bars represent the SD from six replicates. P values were analyzed using the student's t test (*** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001).