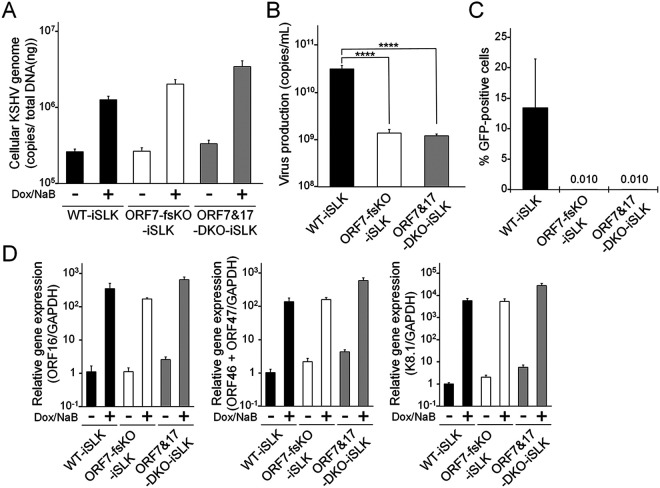
FIG 6.
Characterization of ORF7-KO-KSHV and ORF7&17-DKO-KSHV. (A) Quantification of intracellular viral DNA (genome replication). WT-iSLK, ORF7-fsKO-iSLK, and ORF7&17-DKO-iSLK cells were treated with Dox and NaB to induce the lytic phase. Next, the intracellular viral DNA levels were measured using qPCR and were normalized to the total amount of DNA. (B) Quantification of extracellular encapsidated KSHV genomes. WT-iSLK, ORF7-fsKO-iSLK, and ORF7&17-DKO-iSLK cells were treated with Dox and NaB to induce the lytic phase and the culture supernatants were harvested. The encapsidated KSHV genome levels in the culture supernatants were measured using qPCR. ****, P < 0.001. (C) Measurement of infectious virus. WT-iSLK, ORF7-fsKO-iSLK, and ORF7&17-DKO-iSLK cells were treated with Dox and NaB to induce the lytic phase and the culture supernatants were harvested. Progeny virions from the cell supernatants were used to infect fresh HEK293T cells, and GFP-positive cells were counted by flow cytometry at 24 h postinfection. (D) Analysis of mRNA expression of KSHV lytic genes: IE, ORF16; E, ORF46 and ORF47; and L, K8.1. Total RNA was purified from lytic-induced iSLK cells and was subjected to qRT-PCR. The evaluated lytic gene mRNA levels were normalized to the GAPDH mRNA levels. The values obtained from Dox- and NaB-untreated WT-iSLK cells were defined as 1.0.