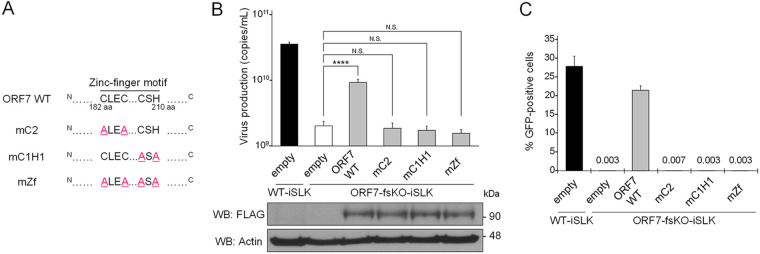
FIG 8.
The conserved zinc-finger motif within ORF7 is essential for the recovery of suppressed virus production in ORF7-fsKO-iSLK cells. (A) The zinc-finger of ORF7, which binds to zinc ion, is speculated to be formed by three Cys and one His (i.e., C182, C185, C208, and H210) within the zinc-finger motif (C182-H210). Three expression plasmids encoding ORF7 zinc-finger mutants, along with a 3xFLAG tag were constructed. These mutations comprised the following amino acid substitutions: mC2 (C182A, C185A), mC1H1 (C208A, H210A), and mZf (C182A, C185A, C208A, H210A). (B) The effects of exogenous ORF7 zinc-finger mutants on suppressed extracellular encapsidated viral genome levels in ORF7-fsKO-iSLK cells. ORF7-fsKO-iSLK cells were transfected with ORF7 WT or ORF7 zinc-finger mutant plasmids and were simultaneously cultured with Dox and NaB for 72 h to induce the lytic phase. The culture supernatants were harvested and the levels of encapsidated KSHV genomes were determined by qPCR. In order to confirm the expression of ORF7 WT or the ORF7 mutants transfected and lytic-induced iSLK cells were lysed and subjected to Western blotting with anti-FLAG antibody (FLAG). Antibodies directed against β-actin (Actin) were used as a loading control. N.S., not significant (P > 0.05); ****, P < 0.001. (C) The effects of exogenous ORF7 zinc-finger mutants on suppressed infectious virus production in ORF7-fsKO-iSLK cells. ORF7-fsKO-iSLK cells were transfected with ORF7 WT or the ORF7 mutants and were simultaneously cultured with Dox and NaB for 72 h to induce the lytic phase. The culture supernatants were harvested and were inoculated into fresh HEK293T cells to monitor infectivity. At 24 h postinfection, GFP-positive cells were counted by flow cytometry.