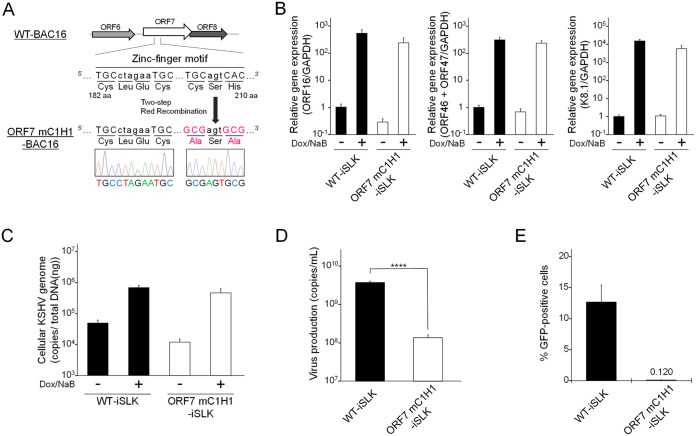
FIG 9.
Construction and characterization of ORF7 mC1H1 KSHV. (A) Schematic illustration of the genetic locus of ORF7 and the mutation added to WT-BAC16 for construction of ORF7 mC1H1-BAC16. The neighboring DNA sequence of the additional mutation in ORF7 mC1H1-BAC16 was confirmed by Sanger sequencing. (B) Measurement of mRNA expression levels of viral lytic genes: IE, ORF16; E, ORF46 and ORF47; L, K8.1 in lytic-induced WT-iSLK and ORF7 mC1H1-iSLK cell lines. iSLK cells were treated with Dox and NaB for 72 h to induce the lytic phase, and total RNA was subjected to qRT-PCR. The mRNA levels of the tested lytic genes were normalized to the GAPDH mRNA levels. The values obtained from Dox- and NaB-untreated WT-iSLK cells were defined as 1.0. (C) Quantification of intracellular viral DNA (genome replication). iSLK cells were treated with Dox and NaB to induce the lytic phase. The intracellular viral DNA levels were measured using qPCR and were normalized to the total amount of DNA. (D) Quantification of extracellular encapsidated KSHV genome levels. iSLK cells were treated with Dox and NaB to induce the lytic phase. The culture supernatants were harvested and were assayed using qPCR to quantitate the encapsidated KSHV genome levels. ****, P < 0.001. (E) Measurement of infectious virus released from lytic-induced iSLK cells. iSLK cells were treated with Dox and NaB to induce the lytic phase and the culture supernatants were harvested. Progeny virions in the supernatants were used to infect fresh HEK293T cells, and GFP-positive cells were counted by flow cytometry at 24 h postinfection.