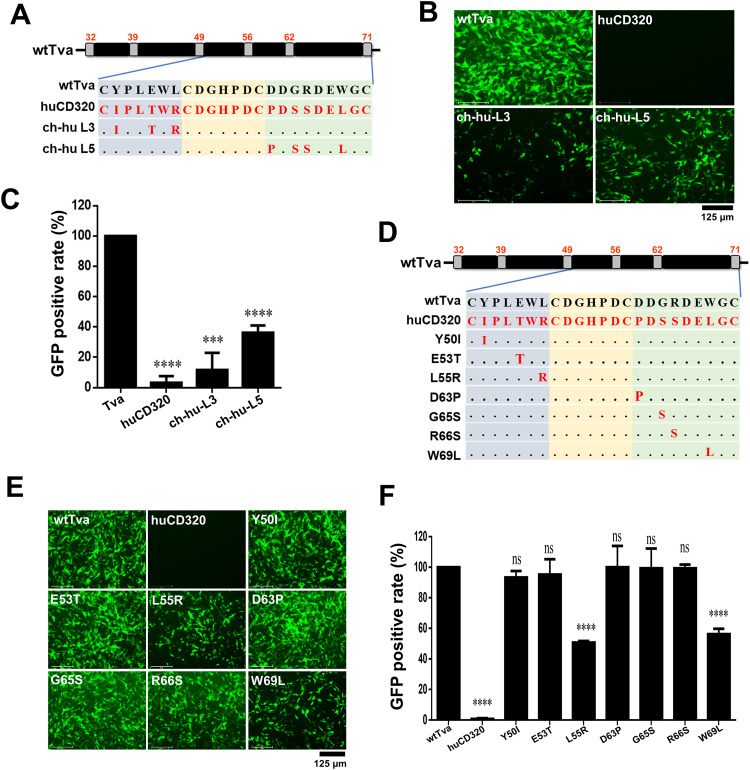
FIG 3.
L55 and W69 of Tva were the key residues for virus entry. (A) Schematic diagram of the strategy used for constructing chimeric Tva receptors with the L3 or L5 fragment of the LDL-A module substituted with the corresponding fragment of huCD320. (B and C) Entry of RCASBP(A) virus into DF-1-TvaKO cells expressing the chimeric Tva receptors. (B) Virus entry levels as analyzed by fluorescence microscopy at 72 hpi. Scale bar: 125 μm. (C) Virus entry levels as analyzed by counting the proportion of GFP-positive cells using flow cytometry at 72 hpi. (D) Schematic diagram of the strategy used for constructing chimeric Tva receptors with seven different single-residue substitutions. (E and F) Entry of RCASBP(A) virus into DF-1-TvaKO cells expressing the chimeric Tva receptors. (E) Virus entry levels as analyzed by fluorescence microscopy at 72 hpi. Scale bar: 125 μm. (F) Virus entry levels as analyzed by counting the proportion of GFP-positive cells using flow cytometry at 72 hpi. Data from three independent experiments are shown as means ± standard deviations of triplicates. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, no significant difference.