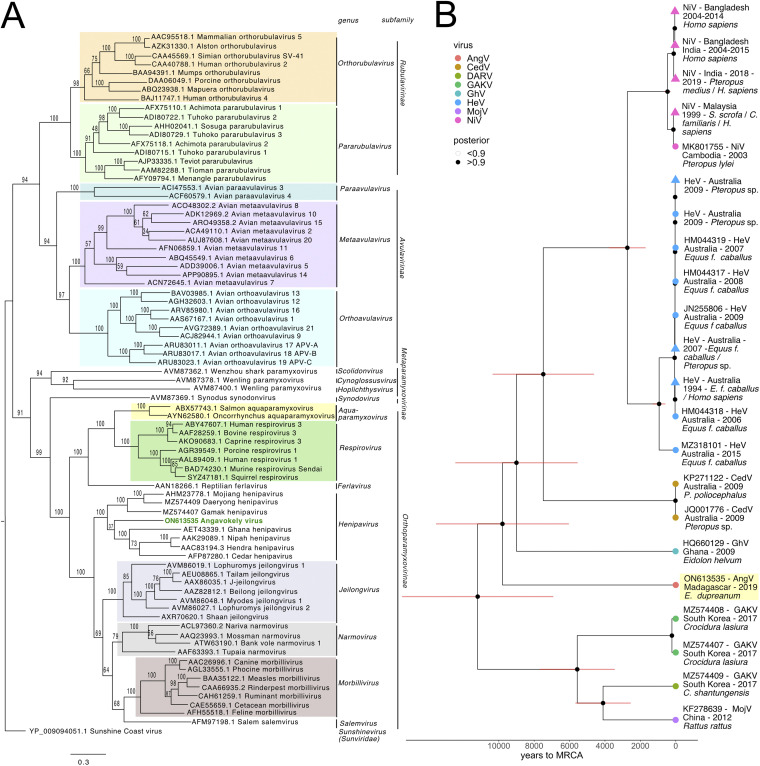
FIG 4.
(A) Phylogenetic analysis of the complete L protein sequences of members of the family Paramyxoviridae. We note that the sequence for the newly described Langya henipavirus (LayV) (12) was not yet available at the time of this writing and is, therefore, not included in the phylogenies. Tree is rooted with Sunshine Coast Virus (GenBank accession number: YP_009094051.1) as an outgroup, with outgroup branch length shrunk for ease of viewing. Novel HNV, AngV, is depicted in green. Subfamilies and genera are demarcated, excluding those unassigned to subfamily (genera Scolidonvirus, Cynoglossusvirus, Hoplichthysvirus). Bootstrap support is depicted and GenBank accession numbers displayed next to virus names. Scale bar represents substitutions per site. (B) Time-resolved Bayesian phylogeny computed in BEAST 2 incorporating all available Henipavirus whole-genome nucleotide sequences, with the addition of newly discovered GAKV, DARV, and AngV. Closely related sequences are collapsed at triangle nodes for NiV and HeV (phylogeny with uncollapsed branches available in Fig. S2 in the supplemental material). HPD intervals of 95% around the timing of each branching node are visualized as red horizontal bars. Posterior support of >0.9 is indicated by black coloring of the corresponding node, and distinct Henipavirus species are indicated by colored tip points, with AngV highlighted in yellow for further emphasis. The estimated time to MRCA for Angavokely virus and the previously described bat-borne HNVs is 9,794 (95% HPD 6,519 to 14,025) years ago.