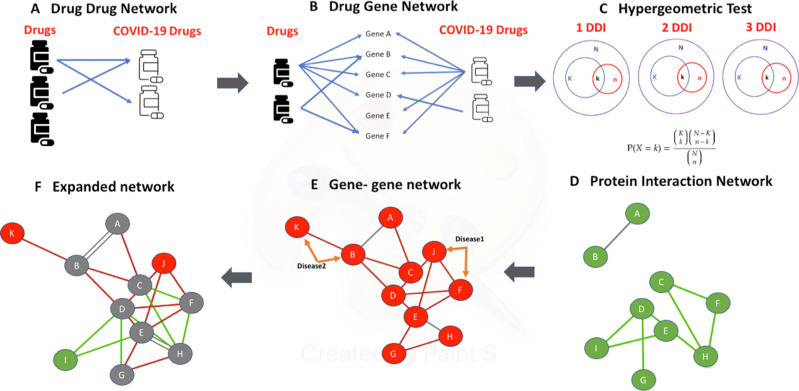
Fig. 1. Methodology workflow.
A A list of Drug-Drug Interactions (DDIs) with COVID-19 treatments and recorded clinical adverse effects from the Liverpool dataset was created (B) PGx information from PharmGKB was extracted for each drug participating in a DDI to build a drug-gene interaction list. C For each drug–drug interaction (DDI), a hypergeometric test was performed (Fisher test, p-value < 0.05 to determine the statistical significance of having overrepresented common genes in both drugs of the same co-medication with a clinical interaction. D Significant DDIs (p-value < 0.05) are selected, and their gene list has been used as input in the STRING database to find curated interactions between drug-interacting genes of each DDI. E Gene-disease associations of the above identified genes, based on GWAS, OMIM and GAD datasets, were retrieved and a new, sheared-disease gene-gene network was constructed with edges depicting genes associated with a common disease. F Networks of (D) and (E) are combined together providing an expanded PGx biomarker network that shows statistically significantly associated genes with COVID-19 treatment adverse effects.