Extended Data Fig. 9 |. Hippocampal single-nucleus transcriptome analysis comparing OrganEx to other experimental conditions.
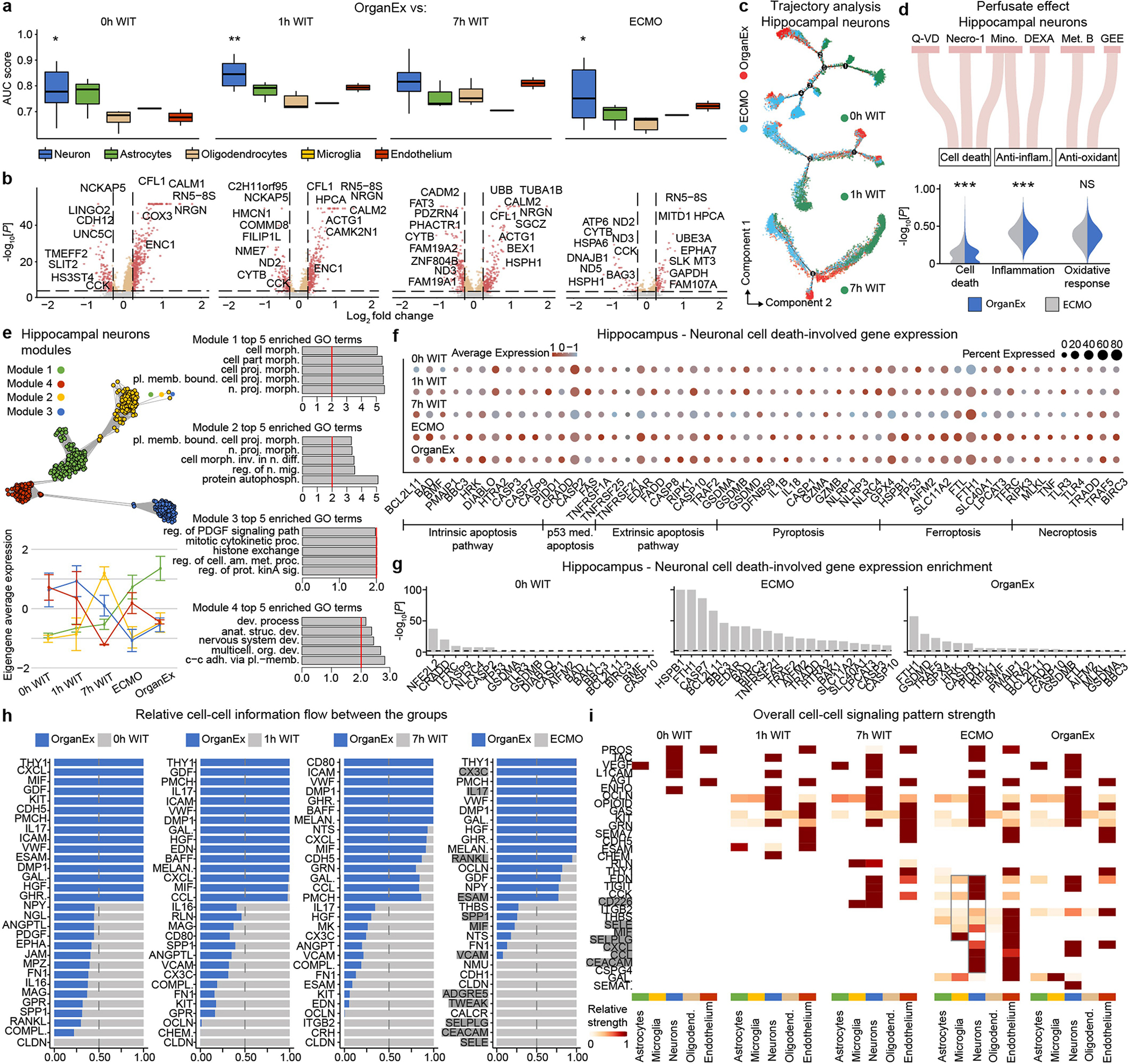
a, AUC scores of the Augur cell type prioritization between OrganEx and other groups. b, Volcano plot showing DEGs in hippocampal neurons between OrganEx and 0h WIT, 1h WIT, 7h WIT, and ECMO. c, Trajectories of hippocampal neurons. Colour indicates different experimental groups. d, Sankey plot showing perfusate components and violin plots showing their effects on hippocampal neurons between the OrganEx and ECMO groups. e, Hierarchical clustering of the top DEGs across experimental groups and derived functional gene modules (upper left). Eigengene average expression trends exhibit distinct trends between ECMO and OrganEx groups (lower left) of modules whose enriched GO terms are predominantly related to cellular function (right) (Supplementary Table 5). f, Expression of the genes involved in cell-death pathways in neurons. g, Gene expression enrichment of the genes involved in cell-death pathways in neurons. h, Stacked bar plot showing relative information flow for each signalling pa pathway across experimental group pairs. Significant signalling pathways were ranked based on differences in the overall information flow within the inferred networks between OrganEx and 0h WIT, 1h WIT, 7h WIT, and ECMO. Genes important in inflammation are highlighted grey. i, Overall signalling patterns across all experimental conditions. Genes important in inflammation are highlighted grey. Necro-1, necrostatin-1; Mino, minocycline; DEXA, dexamethasone; Met. B, methylene blue; GEE, Glutathione Ethyl Ester. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, NS: not significant.
