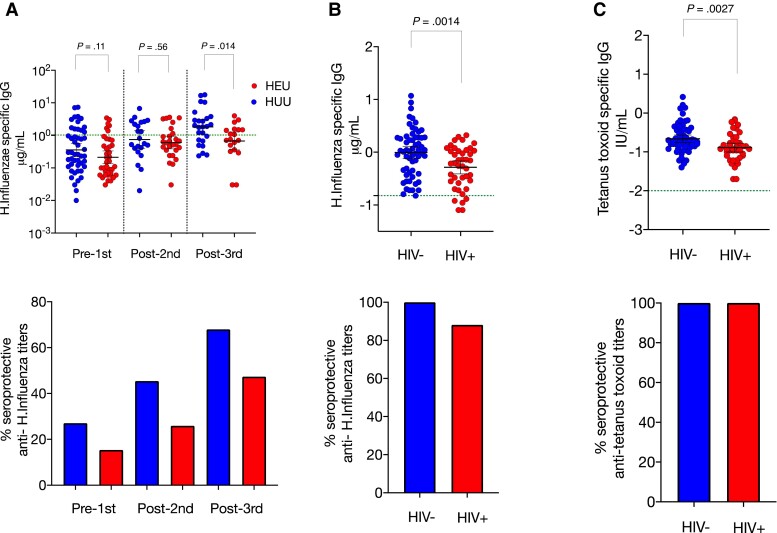
Figure 4.
Infant and maternal antibody responses. Preceding and after Penta-DTwPHibHepB vaccination, we measured vaccine titers using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to (A) anti-Hib immunoglobulin G (IgG) in infant serum at 5–7 (human immunodeficiency virus-unexposed uninfected [HU], n = 50; human immunodeficiency virus-exposed uninfected [HEU], n = 39), 14–15 (HU, n = 22; HEU, n = 27), and 18–23 (HU, n = 25; HEU, n = 19) weeks; we also measured (B) maternal anti-Hib IgG (C) maternal anti-TT IgG at 1 timepoint in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-uninfected (n = 61) and HIV-infected (n = 43). Blue circles are controls and red are HEU infants or HIV-infected mothers. Green dotted horizontal line represents cutoff for protective titers. Data are presented as mean (95% confidence interval) and analyzed using Mann-Whitney U test. Minimum putative protective titers are 0.15 µg/mL (passive) and 1.0 µg/mL (acquired) for Hib [30] and 0.01 IU/mL for tetanus toxoid and diphtheria toxoid.