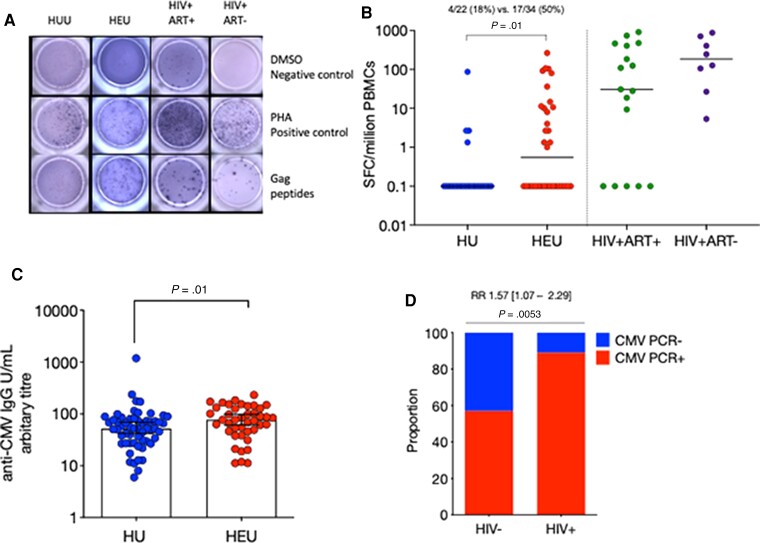
Figure 5.
Infant exposure to immune-modulating viruses human cytomegalovirus (CMV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). (A) Detection of Gag-specific T cells by T-cell enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISpot) assay in human immunodeficiency virus-unexposed uninfected (HU) and human immunodeficiency virus-exposed uninfected (HEU) infants and antiretroviral therapy (ART)-naive/experienced HIV-infected adults. Isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were incubated with 15-mer Gag peptide pool, phytohemagglutinin (PHA) as a positive control, or Roswell Park Memorial Institute media as a negative control. Interferon-γ-producing cells were detected on a 96-well microtiter ELISpot plate. (B) The frequency of spot-forming cells (SFCs)/million PBMCs are plotted for all subjects. Data were analyzed using Fisher’s exact test (HU, n = 22; HEU, n = 34; HIV+ART+, n = 17; HIV+ART−, n = 8). (C) Plasma anti-human cytomegalovirus (CMV) immunoglobulin G (IgG) was measured in infants between 5 and 15 weeks of age and assigned an arbitrary titer. The proportion of (D) HIV-infected and uninfected mothers with reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detected CMV deoxyribonucleic acid in their breast milk, (HIV−, n = 23; HIV+, n = 35). The IgG data were analyzed using Mann-Whitney U test reported as medians (interquartile range) and PCR data using a Fisher’s exact test reporting effective size as a relative risk (RR). Blue circles are HU controls and red circles are HEU. Data are presented as means (standard deviation). DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.