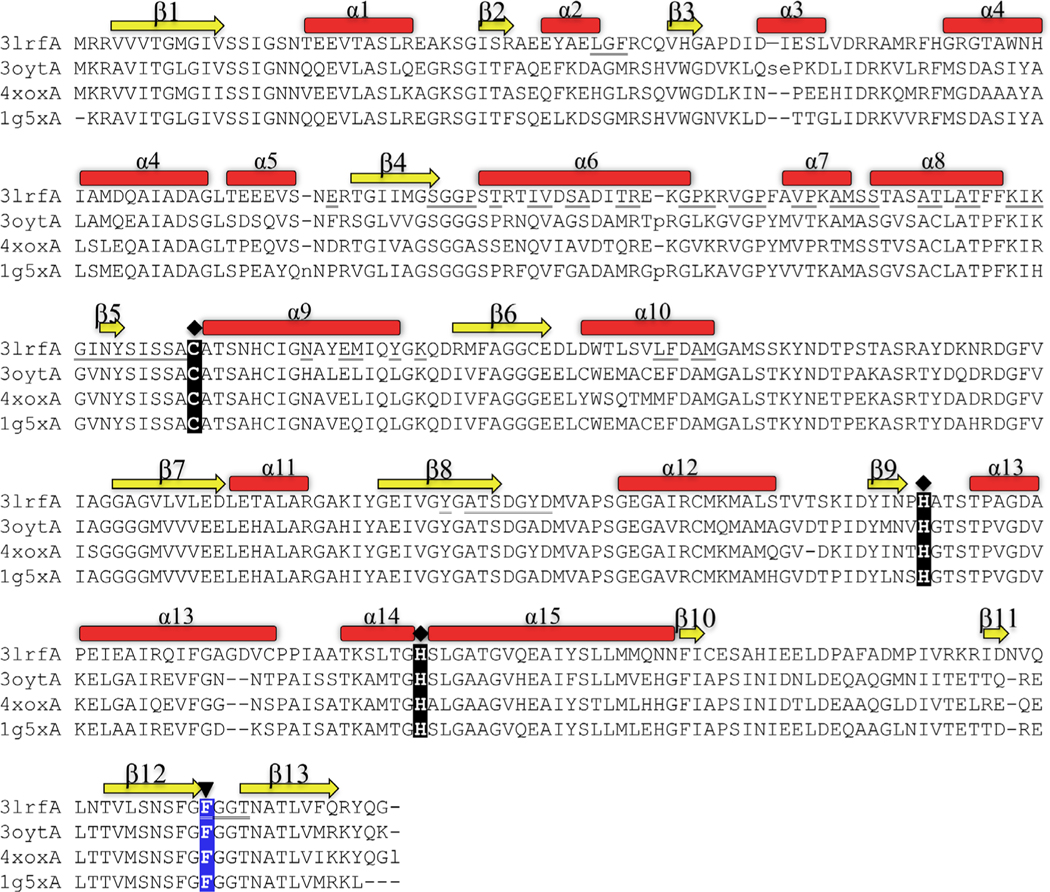
FIGURE 2.
Structural alignment of the most closely related structures in the PDB. 3lrfA is the β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase I from Brucella melitensis in this study. 3oytA is the β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase I from Yersinia pestis (r.m.s.d 0.8 Å, sequence identity 56%). 4xoxA is the β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase I from Vibrio cholera (r.m.s.d 0.8 Å, sequence identity 64%) and 1g5x is the β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase I from Escherichia coli (r.m.s.d 0.8 Å, sequence identity 61%. The catalytic active site residues (Cys, His, His) are highlighted with a diamond-shaped symbol, and the highly conserved Phe residue at the end of β12 (highlighted with an upside-down triangle) mediates substrate specificity and entry of an acyl chain to the binding cavity. β-Sheets are displayed yellow; α-helices are displayed red. Underlined residues indicate residues at the dimer interface (see also Figure 3B) [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]