Figure 2.
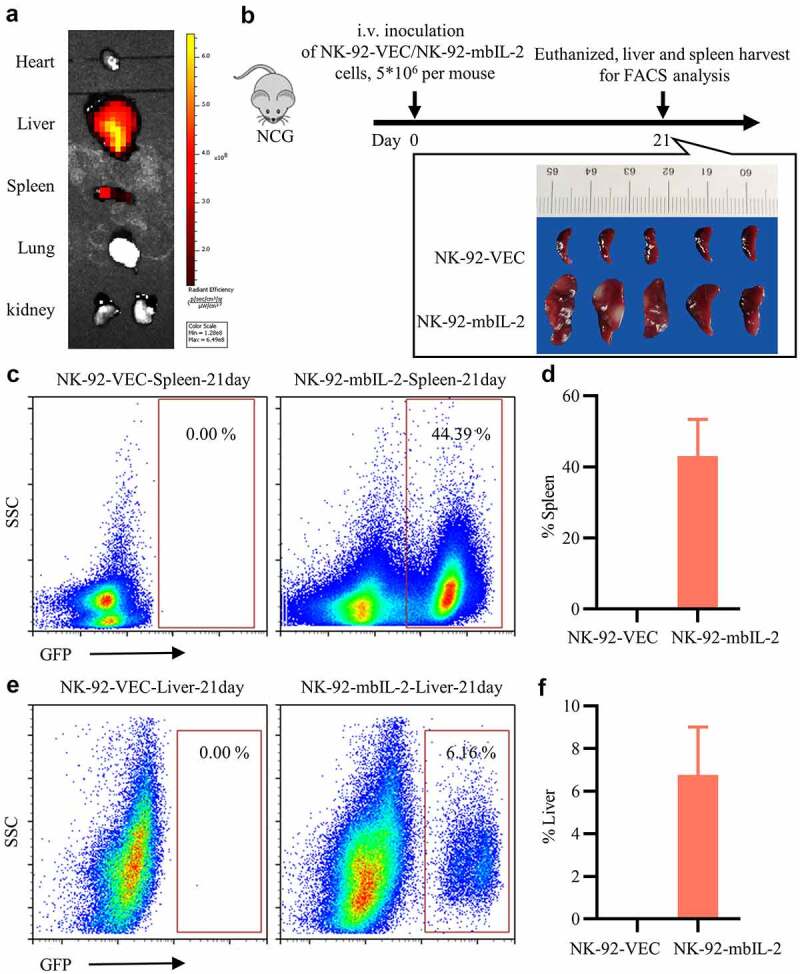
MbIL-2 supports NK-92 cells long-term persistence in vivo.
a: Representative fluorescence images of mice after intravenous injection of DiR-labeled NK-92-mbIL-2 cells after three days. b: NCG mice implanted intravenously with NK-92-VEC or NK-92-mbIL-2 cells. The mice were sacrificed 21 days after transplantation for analysis. NK-92-VEC maintained with 200 U/ml IL-2 and NK-92-mbIL-2 maintained without IL-2 in vitro for experiments. c: Representative flow cytometry analysis showing the proportion of NK-92-VEC or NK-92-mbIL-2 cells residing in the spleen. d: Quantification and statistical analysis of the data in C (n = 5). e: Representative flow cytometry analysis showing the proportion of NK-92-VEC or NK-92-mbIL-2 cells residing in living cells. f: Quantification and statistical analysis of the data in E (n = 5).
