Figure 7.
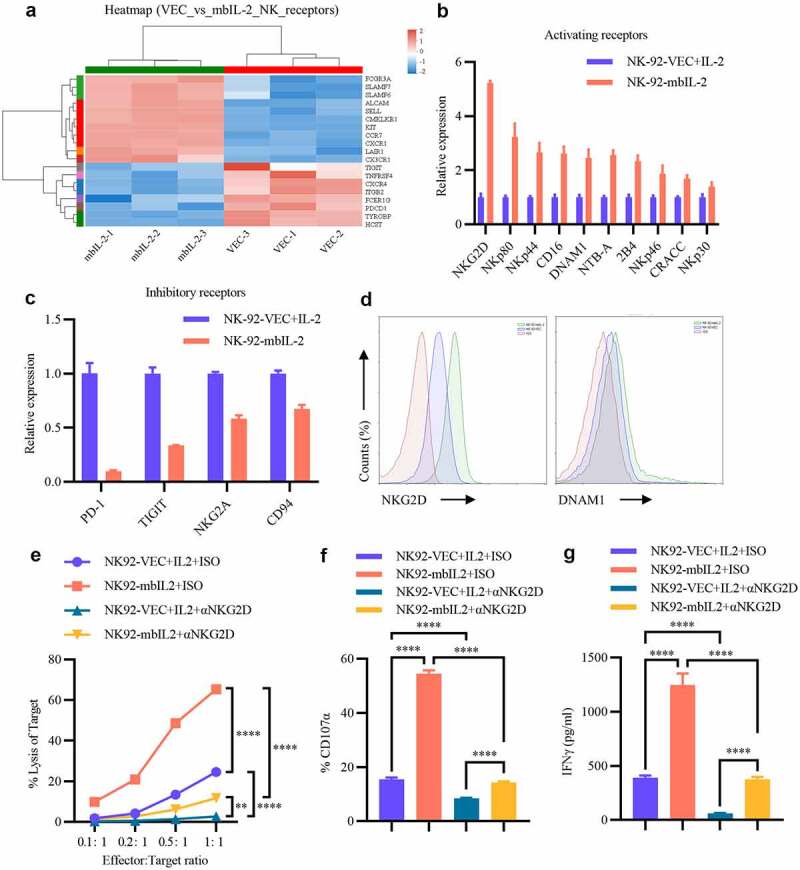
MbIL-2 regulates receptor repertoire to enhance NK cell cytotoxicity.
a: Unsupervised cluster analysis of NK cell receptors in NK-92-VEC cells and NK-92-mbIL-2 cell transcriptome profiles (n = 3). NK-92-VEC maintained with 200 U/ml IL-2 and NK-92-mbIL-2 maintained without IL-2 for RNA-sequencing. b: qPCR analysis of NK cell activating receptor gene expression in NK-92-VEC and NK-92-mbIL-2 cells (n = 3). NK-92-VEC maintained with 200 U/ml IL-2 and NK-92-mbIL-2 maintained without IL-2 for assays. c: qPCR analysis of NK cell inhibitory receptor gene expression in NK-92-VEC and NK-92-mbIL-2 cells (n = 3). NK-92-VEC maintained with 200 U/ml IL-2 and NK-92-mbIL-2 maintained without IL-2 for assays. d: Flow cytometric analysis of NKG2D and DNAM1 expression in NK-92-VEC and NK-92-mbIL-2 cells. NK-92-VEC maintained with 200 U/ml IL-2 and NK-92-mbIL-2 maintained without IL-2 for assays. e: Direct lysis of NK cells against target cell K562. Effector cells were blocked with NKG2D antibody or isotype antibody for 1 h and then co-incubated with the target cells for 4 h at the indicated effector: target ratio. Flow cytometric analysis of the proportion of GFP−7-AAD+ cells (n = 3). At the co-culture time, exogenous IL-2 was added to the NK-92-VEC cells and not added to the NK-92-mbIL-2 cells for assays. f: Flow cytometric analysis of the proportion of GFP+-CD107α+ cells after NK cells were blocked by NKG2D antibody or isotype antibody for 1 h co-incubation with target cells at 1:1 for 12 h (n = 3). At the co-culture time, exogenous IL-2 was added to the NK-92-VEC cells and not added to the NK-92-mbIL-2 cells for assays. g: ELISA data showing the release of IFN-γ by NK cells blocked by the NKG2D antibody or isotype antibody for 1 h after co-incubation with target cells at 1:1 for 5 h (n = 3). At the co-culture time, exogenous IL-2 was added to the NK-92-VEC cells and not added to the NK-92-mbIL-2 cells for assays.
