Figure 1.
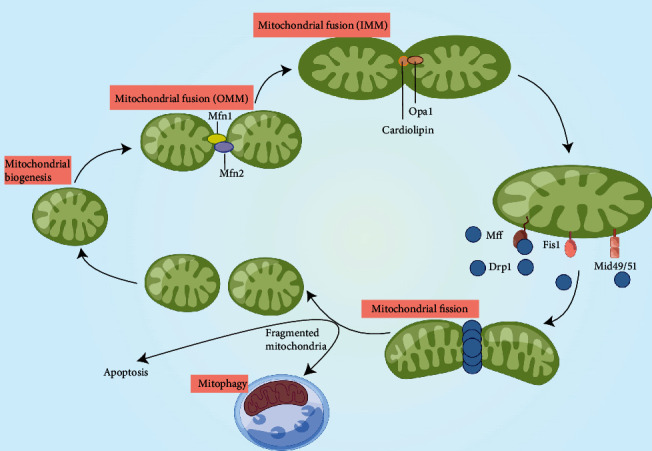
Regulatory mechanisms of mitochondrial dynamics. Mitochondria constantly undergo a dynamic cycle of fission and fusion. The fusion of two neighboring mitochondria depends on homo- and heterotypic interactions between Mfn 1/2 on the OMM. Following OMM fusion, IMM fusion is mediated by OPA1, which contains a cardiolipin- (CL-) binding site that interacts with the CL located on the IMM. During mitochondrial fission, phosphorylated Drp1 is recruited to the OMM via interaction with specific receptors, including Mff, Fis1, and Mid 49/51. The recruited Drp1 forms ring-like structures that constrict the organelle and produce two individual daughter mitochondria. During fission, impaired or dysfunctional components can be separated from the mitochondrial network and then degraded by mitophagy. However, mitochondrial fragmentation, resulting from excessive mitochondrial fission, can result in apoptosis by inducing mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) and release of intermembrane space (IMS) proteins such as cytochrome c, mitofusins 1/2 (Mfn 1/2), optic atrophy protein 1 (OPA1), dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1), mitochondrial fission factor (Mff), fission protein 1 (Fis1), and mitochondrial dynamic proteins of 49 and 51 kDa (Mid 49/51).
