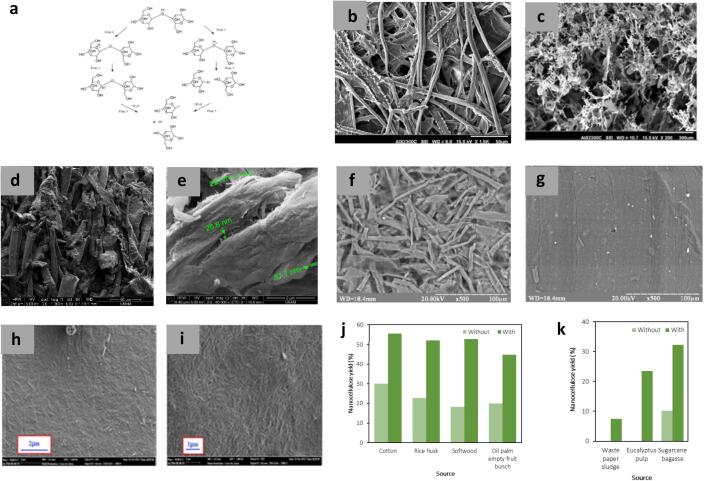
Fig. 7.
(a) Mechanism of acid hydrolysis [82]. SEM images of (b, c) rice straw after chemical pretreatment and nanocellulose after high-speed homogenization and ultrasonication [47] (d, e) non-sonicated and sonicated CNC from cotton [83] (f, g) organosolv straw pulp after hydrolysis and after ultrasonic-assisted hydrolysis [84] (h, i) CNC after hydrolysis and after ultrasound-assisted hydrolysis [85]. Enhancement in nanocellulose yield from various cellulose sources after ultrasound assistance using (j) conventional acid hydrolysis [86], [87], [88], [89], [90], [91], [92] and (k) weak acid hydrolysis [93], [94], [95].