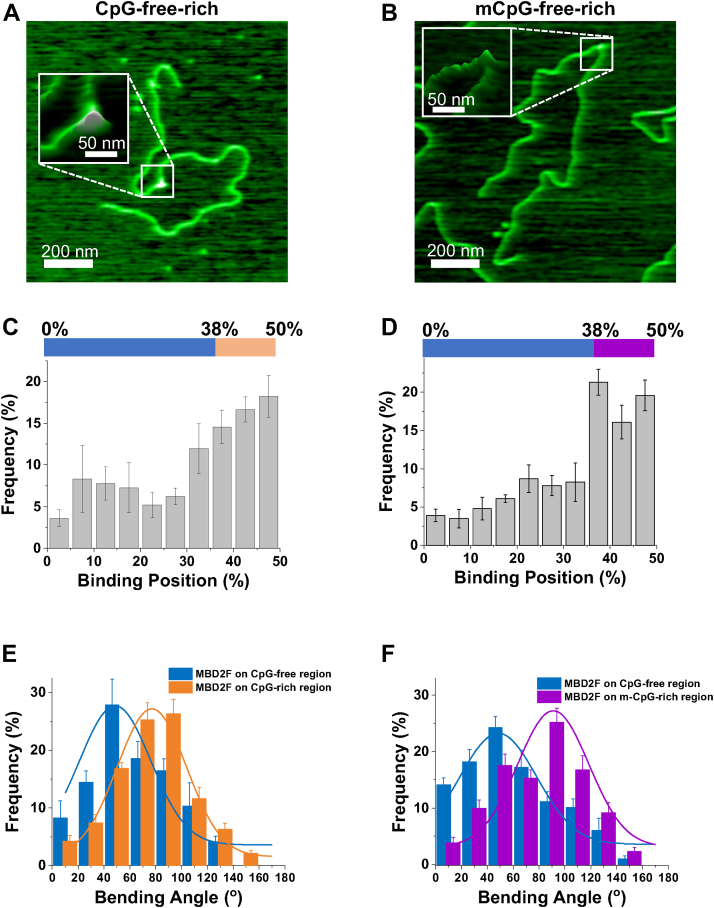
Figure 4.
MBD2sc induces DNA bending upon binding to CpG-free–rich and mCpG-free–rich DNA substrates. Representative AFM images of MBD2sc on the linear CpG-free–rich (A) and on mCpG-free–rich DNA (B). The XY scale bar is 200 nm. Inset: an expanded 3-D image of the indicated region. C and D, analysis of the binding position of MDB2sc on the linear CpG-free–rich (C) and mCpG-free–rich (D) substrates. Over 49% of MBD2sc (N = 95 out of 192) binds to the CpG-rich region (38% to 50%) (C) and 60% of MBD2sc (N = 131 out of 230) binds to the mCpG-rich region (D). E and F, DNA-bending angles induced by MBD2sc upon binding to the CpG-free region (49° ± 28°, mean ± SD, N = 97) and CpG-rich region (77° ± 27°, N = 95) on the CpG-free–rich DNA and upon binding to the CpG-free region (49° ± 30°, N = 99) and m-CpG–rich region (91° ± 27°, N = 131) on the mCpG-free–rich DNA (F). MBD, methyl-CpG–binding domain; CpG, cytosine-guanosine dinucleotide; mCpG, methylated CpG.